Unlocking Fat Metabolism: The AMPK Pathway & Mitochondrial Connection
Connection
AMPK and Mitochondria in Fat Metabolism
In functional medicine, the AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) pathway is a key player in energy regulation, mitochondrial function, and fat metabolism. Often called the body’s “master metabolic switch,” AMPK helps maintain energy balance by directing how the body produces and uses ATP (adenosine triphosphate). When activated, it enhances fat burning, supports mitochondrial function, and improves overall metabolic health.
How AMPK Influences Fat Metabolism
1. AMPK Activation & Energy Sensing
AMPK is activated when the body experiences low ATP levels, such as during fasting, calorie restriction, exercise, or metabolic stress. It senses an increased AMP/ATP ratio, signaling that energy demand is high. Once activated, AMPK shifts metabolism toward energy conservation and fat oxidation.
2. AMPK’s Role in Fat Burning & Storage Prevention
Inhibiting Fat Storage:
- AMPK inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), an enzyme involved in fatty acid synthesis.
- This reduces malonyl-CoA, which normally blocks carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1), the enzyme responsible for transporting fatty acids into mitochondria.
- More fatty acids are sent to mitochondria for oxidation instead of being stored as fat.
Enhancing Fat Breakdown:
- AMPK promotes hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), which helps break down stored triglycerides into free fatty acids.
- These fatty acids are then transported into mitochondria for beta-oxidation, generating ATP.
3. AMPK & Mitochondrial Biogenesis
- AMPK stimulates PGC-1α (Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha), the key regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis.
- Increased mitochondrial density improves fat oxidation and energy efficiency, crucial for endurance performance and metabolic health.
4. AMPK & Insulin Sensitivity
- AMPK increases GLUT4 translocation, allowing muscle cells to absorb more glucose, improving insulin sensitivity.
- By reducing chronic inflammation and increasing mitochondrial efficiency, AMPK prevents lipotoxicity—the buildup of fat in non-adipose tissues that contributes to metabolic dysfunction.
Using PNOE Metabolism Testing to Analyze Fat Oxidation
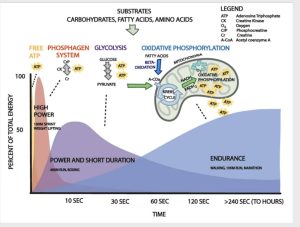
PNOE metabolism testing allows us to measure fat oxidation rates at rest and during exercise, providing valuable insights into metabolic flexibility and efficiency. By analyzing real-time oxygen consumption (VO2), carbon dioxide production (VCO2), and respiratory exchange ratio (RER), we can determine:
- How efficiently the body is using fat vs. carbohydrates for fuel.
- The impact of exercise intensity on fat oxidation.
- The metabolic efficiency of mitochondria in energy production.
Integrating PNOE Data with Nutritional Therapy & Functional Lab Testing
By combining PNOE metabolic data with nutritional therapy assessments and functional lab testing, we can create a comprehensive metabolic profile to:
- Personalize macronutrient intake to optimize fat oxidation.
- Address underlying metabolic inefficiencies.
- Identify potential hormonal imbalances, micronutrient deficiencies, or gut health issues affecting metabolism.
- Track improvements in metabolic flexibility over time with targeted interventions.
How to Activate AMPK & Enhance Mitochondrial Function
1. Exercise
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT) and endurance exercise naturally activate AMPK and boost mitochondrial biogenesis.
2. Nutritional Strategies
- Intermittent fasting & time-restricted eating trigger AMPK activation.
- Low-carb, keto, or targeted carbohydrate cycling enhances metabolic flexibility.
- Polyphenol-rich foods (e.g., berberine, resveratrol, quercetin) mimic AMPK activation and improve mitochondrial health.
3. Supplements for AMPK Activation
- Berberine & Metformin: Mimic the effects of exercise on AMPK.
- Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) & Magnesium: Support mitochondrial function and insulin sensitivity.
- CoQ10 & PQQ: Enhance mitochondrial energy production and efficiency.
4. Cold & Heat Exposure
- Cold exposure (cold plunges, cryotherapy) activates AMPK through brown fat thermogenesis.
- Heat exposure (sauna therapy) promotes mitochondrial repair via heat shock proteins.
Do you want to learn more about metabolic optimization?
Stay tuned for more insights on fueling your body for peak performance!
The AMPK and mTOR pathways must be balanced to optimize health, longevity, and performance—a concept often referred to as the Goldilocks Effect.
- AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) promotes fat metabolism, mitochondrial function, and cellular repair, making it crucial for metabolic health, longevity, and endurance. It is activated by fasting, exercise, and calorie restriction.
- mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) drives muscle growth, protein synthesis, and cellular regeneration, which is essential for strength, recovery, and aging well. It is activated by protein intake, strength training, and growth signals.
The Goldilocks Effect:
- Too much AMPK activation (e.g., excessive fasting, caloric restriction, or endurance exercise) can suppress mTOR, leading to muscle loss, impaired recovery, and reduced strength.
- On the other hand, excessive mTOR activation (e.g., constant high protein intake and lack of fasting) can promote aging-related issues like inflammation and reduced cellular repair.
- For optimal aging and performance, a strategic balance is key—cycling between AMPK and mTOR activation through fasting and feeding, endurance and strength training, and strategic supplementation to support both metabolic efficiency and muscle preservation.
How Does AMPK Influences Fat Metabolism?
1. AMPK Activation & Energy Sensing
- AMPK is activated when the body experiences low ATP levels, such as during fasting, calorie restriction, exercise, or metabolic stress.
- It senses an increased AMP/ATP ratio, signaling that energy demand is high.
- Once activated, AMPK shifts metabolism toward energy conservation and fat oxidation.
2. AMPK’s Role in Fat Burning & Storage Prevention
Inhibiting Fat Storage:
- AMPK inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), an enzyme involved in fatty acid synthesis.
- This reduces malonyl-CoA, which normally blocks carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1), the enzyme responsible for transporting fatty acids into mitochondria.
- More fatty acids are sent to mitochondria for oxidation instead of being stored as fat.
Enhancing Fat Breakdown:
- AMPK promotes hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), which helps break down stored triglycerides into free fatty acids.
- These fatty acids are then transported into mitochondria for beta-oxidation, generating ATP.
3. AMPK & Mitochondrial Biogenesis
- AMPK stimulates PGC-1α (Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha), the key regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis.
- Increased mitochondrial density improves fat oxidation and energy efficiency, crucial for endurance performance and metabolic health.
4. AMPK & Insulin Sensitivity
- AMPK increases GLUT4 translocation, allowing muscle cells to absorb more glucose, improving insulin sensitivity.
- By reducing chronic inflammation and increasing mitochondrial efficiency, AMPK prevents lipotoxicity—the buildup of fat in non-adipose tissues that contributes to metabolic dysfunction.
How to Activate AMPK & Enhance Mitochondrial Function
1. Exercise
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT) and endurance exercise naturally activate AMPK and boost mitochondrial biogenesis.
2. Nutritional Strategies
- Intermittent fasting & time-restricted eating trigger AMPK activation.
- Low-carb, keto, or targeted carbohydrate cycling enhances metabolic flexibility.
- Polyphenol-rich foods (e.g., berberine, resveratrol, quercetin) mimic AMPK activation and improve mitochondrial health.
3. Supplements for AMPK Activation
- Berberine & Metformin: Mimic the effects of exercise on AMPK.
- Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) & Magnesium: Support mitochondrial function and insulin sensitivity.
- CoQ10 & PQQ: Enhance mitochondrial energy production and efficiency.
4. Cold & Heat Exposure
- Cold exposure (cold plunges, cryotherapy) activates AMPK through brown fat thermogenesis.
- Heat exposure (sauna therapy) promotes mitochondrial repair via heat shock proteins.
Conclusion
The AMPK pathway is a key regulator of fat metabolism and mitochondrial function, making it a critical target for improving fat loss, metabolic health, longevity, and athletic performance. By incorporating exercise, fasting, nutrition, and targeted supplementation, individuals can optimize AMPK activation, enhance mitochondrial function, and improve their body’s ability to burn fat efficiently.
Want to learn more about metabolic optimization?
Stay tuned for more insights on fueling your body for peak performance!
AMPK and Mitochondria in Fat Metabolism
AMPK influences fat metabolism primarily through its interaction with mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, where fatty acids are oxidized for energy production. Here’s how the connection works:
1. AMPK Activation: Energy Sensing & Fat Oxidation
- AMPK is activated in response to low ATP levels, which can result from fasting, calorie restriction, exercise, or metabolic stress.
- It responds to an increased AMP/ATP ratio, signaling that energy demand is high.
- Once activated, AMPK shifts cellular metabolism towards energy production and conservation, prioritizing ATP generation through fat oxidation.
2. AMPK’s Role in Fat Metabolism
AMPK regulates fat metabolism by:
- Inhibiting Fat Synthesis:
- AMPK inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), an enzyme involved in fatty acid synthesis.
- This reduces malonyl-CoA, which normally inhibits carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1), the key enzyme that transports fatty acids into mitochondria.
- Result: More fatty acids enter mitochondria for oxidation instead of being stored as fat.
- Enhancing Fat Breakdown (Lipolysis & β-Oxidation):
- AMPK promotes hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), which breaks down stored triglycerides into free fatty acids.
- Free fatty acids are then shuttled into mitochondria for β-oxidation, generating ATP.
3. AMPK & Mitochondrial Biogenesis
- AMPK upregulates PGC-1α (Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha), a master regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis.
- More mitochondria = greater capacity for fat oxidation and ATP production.
- This is crucial for metabolic efficiency, especially in endurance athletes or those aiming to improve metabolic flexibility.
4. AMPK & Insulin Sensitivity
- AMPK enhances GLUT4 translocation, increasing glucose uptake in muscle cells.
- Improves insulin sensitivity by reducing chronic inflammation and increasing mitochondrial efficiency.
- Reduces lipotoxicity, preventing excess fat accumulation in non-adipose tissues.
Functional Medicine Approach to Optimizing AMPK & Mitochondrial Health
To support AMPK activation and mitochondrial function, functional medicine focuses on:
- Exercise:
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT) and endurance exercise naturally activate AMPK and boost mitochondrial biogenesis.
- Nutritional Strategies:
- Intermittent fasting & time-restricted eating (stimulates AMPK activation).
- Low-carb/keto approaches & targeted carbohydrate cycling to optimize metabolic flexibility.
- Polyphenol-rich foods (e.g., berberine, resveratrol, quercetin) that mimic AMPK activation.
- Supplements:
- Berberine & Metformin: AMPK activators that improve insulin sensitivity.
- Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) & Magnesium: Support mitochondrial function.
- CoQ10 & PQQ: Enhance mitochondrial energy production.
- Cold & Heat Exposure:
- Cold exposure stimulates AMPK via brown adipose tissue activation.
- Sauna therapy increases heat shock proteins, supporting mitochondrial repair.
Summary:
- The AMPK pathway is a key regulator of fat metabolism and mitochondrial function, making it a target in functional medicine for fat loss, metabolic health, longevity, and athletic performance.
- By supporting AMPK activation through exercise, fasting, nutrition, and targeted supplementation, individuals can enhance mitochondrial efficiency, optimize energy production, and improve metabolic flexibility.
Fasted Zone 1/Zone 2 Workouts – Okay or Not Okay for Women?
Whether fasted Zone 1/Zone 2 training is beneficial or detrimental for women depends on hormonal status (pre-, peri-, or post-menopause) and individual metabolic flexibility. While fasted low-intensity exercise can enhance fat oxidation and metabolic flexibility, it may not be ideal for all women at all life stages.
Pre-Menopausal Women (Reproductive Years) → Caution with Fasting
✅ Pros:
- Women in this phase have higher estrogen, which naturally supports fat oxidation and insulin sensitivity.
- Occasional fasted Zone 2 training may enhance metabolic flexibility if paired with adequate fueling later.
⚠️ Cons & Considerations:
- Too much fasting + endurance training can disrupt hormones (HPA axis dysfunction) → leading to low energy availability, cycle disruptions, or thyroid suppression.
- If fasted training exceeds 60 minutes, cortisol can spike, leading to muscle breakdown and impaired recovery.
- Best approach: Train in a semi-fasted state (small protein intake like collagen, essential amino acids, or a small amount of carbs).
Perimenopausal Women (Hormonal Fluctuations) → More Support Needed
⚖️ Balanced Approach Needed:
- Perimenopause is marked by irregular estrogen and progesterone levels, increasing cortisol sensitivity and insulin resistance.
- Longer fasted Zone 2 sessions can lead to more stress (high cortisol), increased fat storage, and muscle loss.
✅ Best Approach:
- Shorter, low-intensity fasted sessions (≤45 minutes) may be okay if stress is well-managed.
- Prioritize fueling around workouts (especially with protein) to avoid muscle breakdown and metabolic stress.
Post-Menopausal Women (Lower Estrogen & Progesterone) → Fuel First
Avoid Long Fasted Sessions
- With estrogen and progesterone levels dropping, the body’s reliance on fat metabolism decreases.
- Fasting + endurance training can lead to muscle loss, poor metabolic efficiency, and increased stress response.
- Postmenopausal women need more protein and carbs pre-workout to preserve lean mass and metabolic health.
✅ Best Approach:
- Consume protein (~15g) + small carbs (~15-30g) before Zone 2 training for muscle preservation and metabolic support.
- Avoid long fasted workouts—prioritize strategic fueling to maintain muscle and mitochondrial health.
Final Takeaways: Should Women Do Fasted Zone 1/2 Workouts?
- Pre-Menopausal: Okay in moderation (≤60 min), but fuel properly post-workout.
- Perimenopausal: Be cautious—avoid long fasts + endurance training without protein support.
- Post-Menopausal: Fuel before workouts to prevent muscle loss and metabolic decline.
Personalization is key! Use PNOE metabolism testing to assess fat oxidation rates and combine with functional lab analysis (cortisol, glucose, hormones) to determine the best approach for your body.
AMPK Activation, Mitochondrial Function, and Fat Oxidation with Avere-TRIM Ingredients
AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) is a cellular energy sensor and metabolic regulator that plays a crucial role in maintaining energy balance. It enhances mitochondrial biogenesis, fatty acid oxidation, and glucose uptake while inhibiting fat storage and inflammation. Many natural compounds can stimulate AMPK, leading to improved metabolic efficiency, fat oxidation, and mitochondrial function at rest and during exercise.
How AMPK Enhances Fat Oxidation & Mitochondrial Function
- Fat Oxidation: AMPK activation increases fatty acid uptake into the mitochondria by upregulating CPT1 (carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1), which enhances fat oxidation.
- Mitochondrial Biogenesis: AMPK enhances PGC-1α (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha), which stimulates the formation of new mitochondria, improving endurance and energy production.
- Glucose Metabolism: AMPK enhances glucose uptake by increasing GLUT4 translocation, improving insulin sensitivity and energy availability.
- Anti-Inflammatory & Longevity Benefits: By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, AMPK activation supports overall cellular health and longevity.
Determining the minimal effective doses of specific compounds to activate the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway and support mitochondrial function is complex, as it depends on individual factors and the specific health context.
However, based on available research, here are some general insights:
1. Berberine:
- AMPK Activation: Berberine has been shown to activate AMPK, which can improve metabolic health.
- Dosage: Studies have used doses around 500 mg taken two to three times daily.
2. Resveratrol:
- AMPK Activation: Resveratrol, found in red grapes, has been reported to activate AMPK.
- Dosage: Research indicates that doses ranging from 150 mg to 500 mg per day may be effective.
3. Quercetin:
- AMPK Activation: Quercetin, present in many fruits and vegetables, has been reported to activate AMPK.
- Dosage: Effective doses in studies typically range from 500 mg to 1,000 mg per day.
4. Curcumin:
- AMPK Activation: Curcumin, the active component of turmeric, has been reported to activate AMPK.
- Dosage: Studies often use doses between 500 mg and 2,000 mg per day, noting that absorption can be enhanced when taken with black pepper extract (piperine).
5. Green Tea Extract (EGCG):
- AMPK Activation: Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a component of green tea, has been reported to activate AMPK.
- Dosage: Effective doses of EGCG are typically around 400 mg to 500 mg per day.
Supporting Mitochondrial Function: In addition to the compounds mentioned above, other supplements have been identified to support mitochondrial health:
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): Essential for ATP production and acts as an antioxidant within mitochondria.
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA): Supports energy metabolism and helps regenerate other antioxidants.
- Pyrroloquinoline Quinone (PQQ): May promote the growth of new mitochondria and protect against oxidative stress.
- L-Carnitine: Facilitates the transport of fatty acids into mitochondria for energy production.
It’s important to note that individual responses to these supplements can vary, and the optimal dosages may differ based on personal health conditions, age, and other factors. Consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplementation regimen is advisable to ensure safety and efficacy.
Key Phytonutrients in Avere-TRIM and Their Role in AMPK Activation
- Quercetin
- Stimulates AMPK activation and mitochondrial biogenesis.
- Enhances fat oxidation by increasing SIRT1 and PGC-1α activity.
- Improves endurance by reducing oxidative stress and enhancing oxygen utilization.
- Curcumin
- Activates AMPK and promotes mitochondrial function.
- Reduces inflammation and oxidative stress, which can impair metabolic efficiency.
- Enhances fat oxidation by increasing fatty acid mobilization and utilization.
- Berberine
- One of the most potent AMPK activators, often compared to Metformin.
- Increases glucose uptake, reduces insulin resistance, and enhances mitochondrial function.
- Boosts fatty acid oxidation and inhibits fat storage.
- Resveratrol
- Stimulates AMPK and SIRT1, supporting mitochondrial biogenesis and fat metabolism.
- Increases endurance and metabolic flexibility by enhancing energy production.
- Protects against oxidative stress and supports cardiovascular health.
- Green Tea Extract (EGCG)
- Increases AMPK activation and enhances mitochondrial function.
- Stimulates thermogenesis and fat oxidation by upregulating norepinephrine activity.
- Supports metabolic efficiency during exercise and at rest.
- L-Theanine
- Modulates AMPK activation indirectly by reducing stress-related cortisol spikes.
- Supports mitochondrial health by reducing oxidative stress and improving cellular resilience.
- Enhances cognitive function and focus, which may aid in exercise performance.
- Moringa Leaf
- Stimulates AMPK and enhances glucose metabolism.
- Provides polyphenols and antioxidants that support mitochondrial function.
- Supports anti-inflammatory pathways that enhance metabolic health.
Liposomal Delivery & Phosphatidylcholine for Absorption
Avere-TRIM uses a liposomal delivery system with Non-GMO European sunflower phosphatidylcholine to enhance bioavailability and cellular uptake. Phosphatidylcholine supports mitochondrial membrane integrity, optimizing energy production and fat metabolism.
Summary of Benefits for AMPK Activation & Mitochondrial Function
| Ingredient | AMPK Activation | Mitochondrial Support | Fat Oxidation |
| Quercetin | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Curcumin | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Berberine | ✅✅✅ | ✅✅ | ✅✅✅ |
| Resveratrol | ✅✅ | ✅✅✅ | ✅✅ |
| Green Tea (EGCG) | ✅✅ | ✅ | ✅✅ |
| L-Theanine | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Moringa Leaf | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
Effects at Rest vs. During Exercise
- At Rest: AMPK activation increases basal metabolic rate, improves insulin sensitivity, and enhances mitochondrial efficiency.
- During Exercise: Fat oxidation is enhanced, mitochondrial ATP production is optimized, and endurance capacity is improved.
Avere-TRIM’s formulation is strategically designed to activate AMPK, enhance mitochondrial function, and optimize fat oxidation. This is beneficial for metabolic health, endurance, and body recomposition—supporting both performance and longevity. The liposomal delivery system further ensures maximum absorption of these powerful compounds.
Determining the optimal dosages of specific phytonutrients to activate AMPK, enhance mitochondrial function, and promote fat oxidation involves analyzing available research.
Below is a summary of findings for each compound:
- Quercetin
- Dosage: Studies have utilized doses ranging from 500 mg to 1,000 mg per day. Doses up to 1 gram daily have been used safely for up to 12 weeks.
webmd.com
- Curcumin
- Dosage: Effective doses in studies vary, but commonly range from 500 mg to 2,000 mg per day. Curcumin’s bioavailability is low; thus, formulations with enhanced absorption or co-administration with piperine are often used.
- Berberine
- Dosage: Commonly studied doses are 500 mg taken two to three times daily, totaling 1,000 mg to 1,500 mg per day. This regimen has been shown to activate AMPK and improve metabolic parameters.
- Resveratrol
- Dosage: Research indicates that doses between 150 mg to 500 mg per day may be effective. Higher doses are sometimes used, but long-term safety data is limited.
- Green Tea Extract (EGCG)
- Dosage: Effective doses of EGCG range from 400 mg to 800 mg per day. Green tea extracts are generally considered safe even at higher doses, but excessive intake may lead to adverse effects.
mdpi.com
- L-Theanine
- Dosage: Typical doses range from 100 mg to 400 mg per day. L-Theanine is generally well-tolerated and considered safe within this range.
- Moringa Leaf
- Dosage: Research on moringa leaf is less specific regarding standardized dosing. However, studies have used doses ranging from 500 mg to 2,000 mg per day, depending on the extract’s concentration and the study’s focus.
Considerations:
- Bioavailability: Many of these compounds have low natural bioavailability. Utilizing liposomal delivery systems, as mentioned in your formulation, can enhance absorption.
- Safety: While these compounds are generally considered safe, it’s essential to monitor for potential side effects, especially at higher doses. Consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplementation regimen is advisable.
In summary, the dosages mentioned above are based on current research and have been associated with activating AMPK, enhancing mitochondrial function, and promoting fat oxidation. Individual responses may vary, and it’s crucial to consider factors such as bioavailability, potential interactions, and overall health status when determining the appropriate dosage.
Balancing AMPK & mTOR for Optimal Metabolic Health as We Age
As we age, maintaining a balance between AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) and mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) is crucial for metabolic health, fat oxidation, muscle preservation, and longevity. These two pathways function in opposition:
- AMPK promotes fat oxidation, autophagy (cellular cleanup), and mitochondrial efficiency—key for longevity and metabolic flexibility.
- mTOR supports muscle growth, anabolism, and recovery, but excessive activation can lead to insulin resistance, inflammation, and metabolic dysfunction over time.
The challenge? As we age, we become less efficient at activating AMPK while mTOR remains overly stimulated by excess calories, insulin spikes, and sedentary lifestyles—leading to poor metabolic health, increased fat storage, and muscle loss (sarcopenia).
AMPK vs. mTOR: Gender Differences in Aging
Men vs. Women:
- Men typically have greater muscle mass and naturally higher mTOR activation, making them more susceptible to metabolic dysfunction if they overconsume protein or refined carbs.
- Women, particularly postmenopausal women, experience a decline in estrogen, which affects mitochondrial efficiency, AMPK activation, and muscle protein synthesis via mTOR.
- Perimenopausal & menopausal women often need more AMPK activation to maintain metabolic flexibility and avoid increased fat storage, while postmenopausal women need a balance to preserve lean mass.
How to Optimize AMPK & mTOR for Longevity & Metabolic Health
1. Exercise: Activating AMPK & mTOR at the Right Times
- Endurance & Zone 2 Cardio (Low-Intensity Steady State, LISS) → AMPK Activation

- Increases mitochondrial biogenesis and improves fat oxidation.
- Best performed in a fasted or low-glycogen state for maximal AMPK activation.
- HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) & Strength Training → Both AMPK & mTOR Activation
- Short bursts of HIIT activate AMPK for fat metabolism.
- Strength training stimulates mTOR to maintain muscle mass.
- Timing is key: Fasted workouts favor AMPK, while post-workout protein intake boosts mTOR for recovery.
2. Nutrition: AMPK & mTOR in Balance
- Intermittent Fasting & Time-Restricted Eating → AMPK Activation
- Fasting increases AMPK and triggers autophagy, reducing inflammation and metabolic dysfunction.
- Women should aim for a more moderate fasting window (12-14 hours) to avoid hormonal imbalances, while men can typically tolerate longer fasts (16+ hours).
- Protein Intake & Nutrient Timing → mTOR Activation in Moderation
- Strength days: Higher protein (1.6-2.2g/kg) post-workout for muscle maintenance (especially in aging populations).
- Non-strength days: Lower protein, favoring AMPK activation via fasting or plant-based meals.
- For women: Protein timing around workouts is critical to prevent sarcopenia without overactivating mTOR.
- Carbohydrate Cycling → Metabolic Flexibility
- Lower-carb, high-fat intake on endurance or rest days for AMPK activation & fat metabolism.
- Moderate to higher carbs post-exercise on strength days to stimulate mTOR and muscle protein synthesis.
3. Supplements & Nutraceuticals to Boost AMPK & Mitochondria
- Berberine & Metformin → Mimic fasting & exercise effects on AMPK.
- Resveratrol, Quercetin, EGCG (Green Tea Extract) → Support AMPK activation & mitochondrial health.
- PQQ & CoQ10 → Enhance mitochondrial function and energy production.
- Creatine & Leucine → Support mTOR for muscle growth, especially in aging adults.
4. Cold & Heat Therapy to Boost Metabolism
- Cold Exposure (Cold Plunges, Cryotherapy) → AMPK Activation
- Stimulates brown fat thermogenesis & mitochondrial efficiency.
- Sauna & Heat Therapy → Both AMPK & mTOR Activation
- Promotes heat shock proteins for cell repair & metabolic health.
The AMPK and mTOR pathways must be balanced to optimize health, longevity, and performance—a concept often referred to as the Goldilocks Effect.
- AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) promotes fat metabolism, mitochondrial function, and cellular repair, making it crucial for metabolic health, longevity, and endurance. It is activated by fasting, exercise, and calorie restriction.
- mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) drives muscle growth, protein synthesis, and cellular regeneration, which is essential for strength, recovery, and aging well. It is activated by protein intake, strength training, and growth signals.
The Goldilocks Effect:
Too much AMPK activation (e.g., excessive fasting, caloric restriction, or endurance exercise) can suppress mTOR, leading to muscle loss, impaired recovery, and reduced strength. On the other hand, excessive mTOR activation (e.g., constant high protein intake and lack of fasting) can promote aging-related issues like inflammation and reduced cellular repair.
For optimal aging and performance, a strategic balance is key—cycling between AMPK and mTOR activation through fasting and feeding, endurance and strength training, and strategic supplementation to support both metabolic efficiency and muscle preservation.

Using PNOE Metabolism Testing & Functional Lab Analysis for Personalization
To truly optimize metabolic health, we need data-driven insights from:
1. PNOE Metabolism Testing:
- Measures fat oxidation rates at rest and during exercise to determine metabolic flexibility.
- Identifies how efficiently the body is using fat vs. carbohydrates for fuel.
- Tracks improvements in mitochondrial efficiency over time.
2. Functional Lab Testing (FDN-P & FNTP Assessments):
- Hormonal Panel (Cortisol, DHEA, Estrogen, Testosterone, Insulin Sensitivity) → Determines how stress and aging affect AMPK/mTOR balance.
- GI-MAP & Microbiome Analysis → Identifies gut imbalances affecting metabolic function.
- Metabolic & Mitochondrial Markers (Organic Acids Test, Nutrient Deficiencies) → Finds areas where AMPK activation may be impaired.
By combining PNOE metabolic testing with functional lab insights, we can create personalized metabolic health plans, fine-tune exercise and nutrition strategies, and optimize fat oxidation, muscle maintenance, and longevity based on individual needs.
Final Thoughts
- Younger individuals may benefit from more mTOR activation for muscle growth.
- Aging individuals (especially women post-menopause) need more AMPK activation to support fat oxidation and metabolic efficiency, while still incorporating mTOR activation for muscle retention.
- Personalized metabolic testing allows us to balance these pathways effectively for peak performance and longevity.
Want to learn how your metabolism is functioning? PNOE testing + functional lab analysis can reveal your unique fat oxidation rates, metabolic flexibility, and hormonal balance—so you can thrive at any age!