Are you INSULIN RESISTANT?
TEST and NOT GUESS with ULTA Labs if your Doctor will not measure your insulin levels!!

Here are some lab tests that are commonly used to assess insulin resistance:
- Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG): A simple test that measures your blood sugar levels after an overnight fast. Elevated fasting blood glucose levels (typically above 100 mg/dL) can indicate insulin resistance.
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c): This test provides an average of your blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. Elevated HbA1c levels, usually above 5.7%, can be an indicator of insulin resistance and diabetes.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): This involves drinking a sugary solution and then measuring blood sugar levels at specific intervals. Insulin resistance can be indicated by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels during the test.
- Fasting Insulin Levels: Measuring fasting insulin levels alongside fasting blood glucose can help evaluate insulin resistance. Elevated fasting insulin levels can indicate reduced insulin sensitivity.
- Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR): This is a formula that calculates insulin resistance based on fasting glucose and fasting insulin levels. Higher HOMA-IR values suggest greater insulin resistance.
- C-peptide Levels: C-peptide is a marker of insulin production by the pancreas. High levels of C-peptide, especially in the presence of elevated blood sugar, can suggest insulin resistance.
- Triglyceride Levels: Elevated triglyceride levels often accompany insulin resistance and are part of the metabolic syndrome. A triglyceride-to-HDL ratio is sometimes used as an indicator.
- High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Cholesterol Levels: Low HDL cholesterol levels can be associated with insulin resistance.
- Fasting Serum Leptin Levels: Leptin is a hormone that regulates appetite and metabolism. Elevated leptin levels are often seen in individuals with insulin resistance.
- Adiponectin Levels: Adiponectin is a hormone that plays a role in insulin sensitivity. Lower levels of adiponectin are associated with insulin resistance.
- Liver Function Tests: Elevated liver enzymes and markers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) can be indicative of insulin resistance.
- Inflammatory Markers: Elevated levels of inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) are often associated with insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction.
It’s important to note that these tests provide a snapshot of your metabolic health, and a comprehensive evaluation should be conducted by a healthcare professional. Additionally, insulin resistance is often part of a larger picture of metabolic syndrome and can be influenced by genetics, lifestyle, and other factors.
How to reverse insulin resistance in functional medicine
Reversing insulin resistance through functional medicine involves addressing the underlying factors that contribute to the condition. Functional medicine takes a holistic approach, focusing on individualized care and treating the root causes of health issues.
Here’s a general outline of how insulin resistance can be addressed using functional medicine principles:
- Dietary Changes:
- Focus on a whole foods, nutrient-dense diet rich in vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index.
- Reduce or eliminate processed foods, sugary snacks, sugary beverages, and refined carbohydrates.
- Consider incorporating anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, ginger, omega-3 fatty acids, and green tea.
- Balancing Blood Sugar:
- Eat regular meals and snacks to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Avoid large meals that can lead to spikes in blood sugar.
- Include protein and healthy fats with meals to slow down the absorption of carbohydrates.
- Exercise and Physical Activity:
- Engage in regular physical activity, including both aerobic exercise and strength training.
- Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and can lower blood sugar levels.
- Stress Management:
- Chronic stress can contribute to insulin resistance. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and deep breathing.
- Sleep Optimization:
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Poor sleep can disrupt insulin sensitivity.
- Supplements and Nutritional Support:
- Some supplements may help improve insulin sensitivity, such as chromium, magnesium, alpha-lipoic acid, and berberine. Consult a healthcare provider before adding supplements.
- Gut Health and Inflammation:
- Address gut health issues as imbalances in gut bacteria can impact metabolism and inflammation.
- Consider probiotics and a diet that supports a healthy gut.
- Detoxification Support:
- Support the body’s natural detoxification processes by staying hydrated, consuming fiber-rich foods, and supporting liver health.
- Individualized Approach:
- Functional medicine focuses on personalized care. Work with a healthcare provider experienced in functional medicine to create a tailored plan based on your unique health history and needs.
- Monitoring and Adjustments:
- Regularly monitor your progress through lab tests, glucose monitoring, and other relevant assessments.
- Adjust your approach based on your results and how your body responds.
Remember that reversing insulin resistance takes time and commitment. It’s advisable to work with a qualified healthcare provider, such as a functional medicine practitioner or a registered dietitian, to guide you through the process and ensure you’re making safe and effective choices. Functional medicine aims to treat the whole person, so lifestyle, nutrition, and other factors will be considered as part of your treatment plan.
- Low-Carbohydrate Diet: Dr. Bikman has highlighted the benefits of a low-carbohydrate diet for improving insulin sensitivity. He suggests reducing the consumption of refined carbohydrates and sugars, which can lead to chronically elevated insulin levels.
- Healthy Fat Intake: He supports the consumption of healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, olive oil, and fatty fish. These fats can provide sustained energy and may help improve insulin sensitivity.
- Intermittent Fasting: Dr. Bikman has discussed how intermittent fasting and time-restricted eating can help regulate insulin levels and improve insulin sensitivity. These eating patterns can give the body more time to clear excess glucose from the bloodstream.
- Exercise: He emphasizes the importance of regular physical activity, both aerobic exercise and strength training, for improving insulin sensitivity and metabolic health.
- Avoiding Overeating: Dr. Bikman advocates for avoiding overeating, as excess calorie intake can contribute to insulin resistance and obesity.
- Reducing Inflammation: Addressing chronic inflammation through dietary choices and lifestyle changes is important for improving insulin sensitivity. Consuming anti-inflammatory foods and managing stress can play a role in this.
- Personalized Approach: Dr. Bikman often emphasizes that individuals may have different responses to dietary and lifestyle interventions. He encourages people to monitor their own responses to different foods and habits to find what works best for them.
- Metabolic Flexibility: He discusses the concept of “metabolic flexibility,” which is the body’s ability to switch between using glucose and fats for energy. Improving metabolic flexibility can be beneficial for insulin sensitivity.
It’s important to note that while Dr. Ben Bikman’s insights can provide valuable guidance, every individual’s situation is unique. If you’re interested in following his recommendations to reverse insulin resistance, consider consulting with a healthcare professional who can tailor a plan to your specific needs and medical history. Additionally, staying updated with his latest research and presentations will provide the most current information on his views and recommendations.
What is METABOLIC Flexibility as per Dr. Ben Bikman?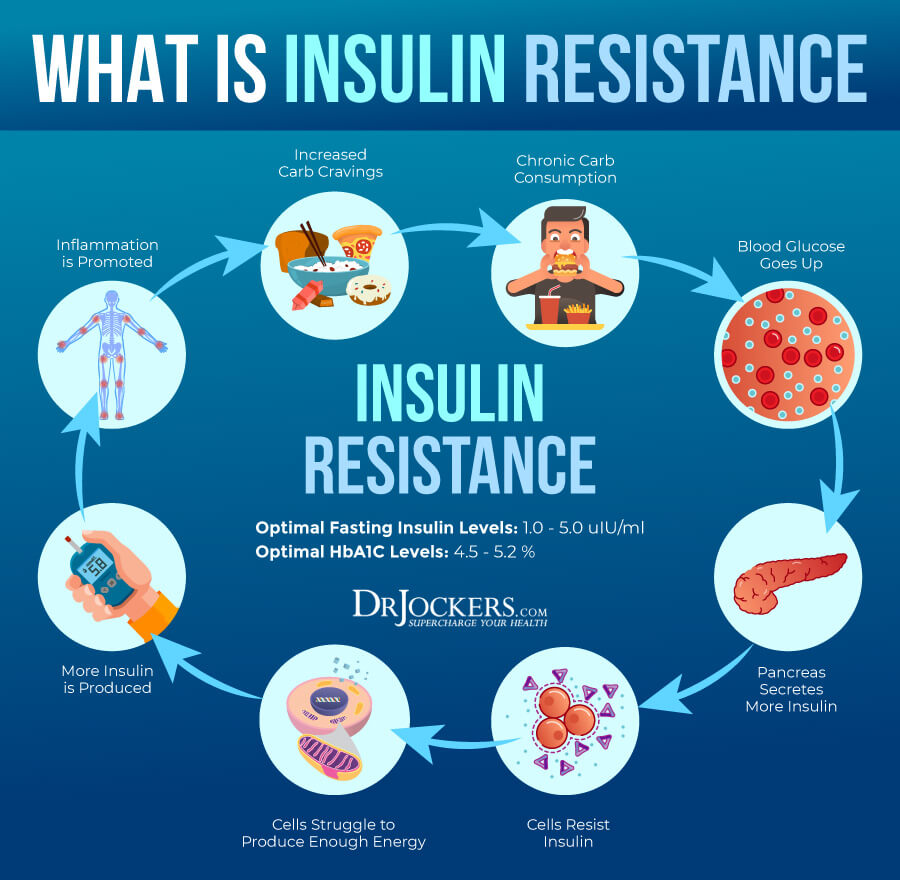
Here’s a more detailed explanation of metabolic flexibility:
- Glucose Utilization: When glucose is available, such as after consuming carbohydrates, a metabolically flexible individual can effectively take up and use glucose for energy. This is important to maintain stable blood sugar levels and provide energy to cells, especially those that rely on glucose as their primary fuel source, like certain parts of the brain.
- Fat Utilization: On the other hand, when glucose availability is low, such as during fasting or low-carbohydrate intake, a metabolically flexible individual can switch to using stored fat as a source of energy. This involves breaking down stored fats into fatty acids, which can then be utilized by various tissues and organs.
- Insulin Sensitivity: Metabolic flexibility is closely linked to insulin sensitivity. Insulin sensitivity refers to how responsive cells are to the effects of insulin, a hormone that regulates glucose uptake by cells. When cells are insulin sensitive, they are better able to take up glucose from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of high blood sugar levels.
- Benefits of Metabolic Flexibility: Metabolic flexibility is associated with improved metabolic health. It allows the body to adapt to different situations, such as variations in food availability and energy demands. It may also play a role in preventing insulin resistance, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. People with good metabolic flexibility are often better equipped to maintain stable energy levels and body weight.
- Factors Affecting Metabolic Flexibility: Various factors can influence metabolic flexibility, including diet, physical activity, genetics, and overall metabolic health. Regular exercise, a balanced diet that includes both carbohydrates and healthy fats, and maintaining a healthy body composition can contribute to better metabolic flexibility.
Dr. Ben Bikman, in his research and presentations, emphasizes the importance of metabolic flexibility as a marker of overall metabolic health. He often discusses how promoting metabolic flexibility through dietary strategies like reducing carbohydrate consumption and improving insulin sensitivity can have positive effects on various health markers, including insulin resistance.
As with any scientific concept, the understanding of metabolic flexibility is continually evolving, so it’s a good idea to refer to Dr. Bikman’s latest work or other reputable sources for the most current insights and research findings on this topic.


