Lumen Basics: Understanding Metabolic Flexibility
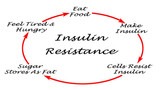
A healthy metabolism is characterized by its ability to efficiently switch between burning carbohydrates and fats for energy, depending on their availability and the body’s energy needs. This adaptability, known as metabolic flexibility, plays a crucial role in determining your overall health. However, what impacts metabolic flexibility can vary greatly from person to person. Factors such as diet, exercise, sleep, and stress all play significant roles.
Lumen is a portable device designed to measure your metabolic flexibility by analyzing the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in your breath. This helps determine whether your body is primarily burning fats or carbohydrates for energy. The key features of Lumen that facilitate this measurement include:
1. Breath Analysis Technology
How It Works:
Lumen uses sensors and breath analysis technology to measure the ratio of carbon dioxide (CO2) to oxygen (O2) in your breath. This ratio is known as the Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER). By analyzing your breath, Lumen provides insights into whether you’re burning more fats or carbohydrates.
Why It’s Important:
The RER value indicates which fuel source your body is predominantly using:
- Higher RER: Indicates a higher proportion of carbohydrates being burned.
- Lower RER: Indicates a higher proportion of fats being burned.
Understanding your current metabolic state helps you tailor your nutrition and lifestyle choices to optimize energy use and metabolic health.
2. Personalized Nutrition and Lifestyle Recommendations
How It Works:
Based on your breath measurements, Lumen provides personalized recommendations for your daily nutrition and activity. These suggestions are tailored to help you achieve specific goals, such as enhancing metabolic flexibility, optimizing workout performance, or supporting weight management.
Why It’s Important:
Metabolic flexibility, the ability to efficiently switch between burning fats and carbohydrates, is a key aspect of metabolic health. Personalized recommendations help you make informed decisions about your diet and exercise, promoting better metabolic efficiency and overall well-being.
3. Daily Metabolic Tracking
How It Works:
Lumen allows you to take multiple measurements throughout the day, including upon waking, before and after meals, and before and after exercise. These readings help track changes in your metabolic state over time.
Why It’s Important:
Continuous tracking provides valuable insights into how different factors (such as diet, exercise, sleep, and stress) impact your metabolism. This helps you identify patterns and make adjustments to improve your metabolic flexibility.
4. App Integration and User Interface
How It Works:
Lumen syncs with a dedicated mobile app that displays your metabolic data, tracks your progress, and offers actionable insights. The app provides a user-friendly interface for setting goals, viewing trends, and receiving personalized tips.
Why It’s Important:
The app’s integration makes it easy to monitor and understand your metabolic health. It provides a convenient way to access your data and apply the insights to your daily life, helping you stay motivated and focused on your goals.
5. Customizable Goals and Feedback
How It Works:
Lumen allows you to set specific health and fitness goals, such as improving metabolic flexibility, losing weight, or enhancing athletic performance. The device and app provide feedback and suggestions based on your progress towards these goals.
Why It’s Important:
Having clear, personalized goals helps you stay motivated and focused on improving your metabolic health. The feedback loop provided by Lumen ensures that you’re continually adjusting your strategies to optimize your metabolism.
Conclusion
The key features of Lumen—breath analysis technology, personalized recommendations, daily metabolic tracking, app integration, and customizable goals—work together to provide a comprehensive understanding of your metabolic flexibility. By measuring whether you’re burning fats or carbohydrates, Lumen helps you make informed decisions about your diet, exercise, and lifestyle, ultimately supporting better metabolic health and overall well-being.
Understanding Metabolic Flexibility and Mitochondrial Health
A healthy metabolism is synonymous with metabolic flexibility—the ability to efficiently switch between burning carbohydrates and fats for energy based on their availability and the body’s energy needs. This flexibility is crucial in determining overall health, and the factors influencing it can vary significantly from person to person. Lumen provides a valuable tool to uncover the hidden connections between your lifestyle choices and your metabolic health, enabling you to make impactful changes.
A common misconception is that burning fat all the time is the hallmark of a healthy metabolism. However, a balanced metabolism should utilize fat during periods of rest and fasting, while relying on carbohydrates for quick energy during intense or sudden activities. This balance is key for optimal health and efficient energy use.
How Lumen Measurement Helps with Mitochondrial Health
Role of Mitochondria in Metabolic Flexibility
Mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell, play a crucial role in metabolic flexibility. They are responsible for converting the nutrients we consume into usable energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The ability of mitochondria to switch between burning fats and carbohydrates is indicative of their health and efficiency.
Lumen’s Role in Monitoring and Improving Mitochondrial Health
Lumen measures the concentration of carbon dioxide in your breath, which provides an indication of whether your body is predominantly burning fats or carbohydrates. This information offers a direct insight into your metabolic state and, by extension, the health and efficiency of your mitochondria.
Why Mitochondrial Health Matters
- Efficient Energy Production: Healthy mitochondria efficiently produce energy by switching between fuel sources as needed. This adaptability is essential for meeting the varying energy demands of daily life and physical activity.
- Reduced Oxidative Stress: Proper mitochondrial function helps minimize the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can cause oxidative stress and damage cellular components, including the mitochondria themselves.
- Improved Metabolic Health: By monitoring your metabolic state, Lumen helps you identify patterns and lifestyle factors that may be affecting your mitochondrial function. For instance, poor sleep, high stress levels, or inadequate nutrition can impair mitochondrial efficiency. By making adjustments in these areas, you can enhance your mitochondrial health, leading to better energy levels, improved physical performance, and overall well-being.
Practical Application with Lumen
With Lumen, you can track how your lifestyle choices—such as diet, exercise, sleep, and stress management—affect your metabolism and mitochondrial function. For example, waking up in fat-burn mode suggests that your mitochondria are effectively using stored fat for energy, which is a sign of good metabolic health. Conversely, consistently waking up in carb-burn mode may indicate a need for lifestyle adjustments to support better mitochondrial efficiency and metabolic flexibility.
Lumen provides a window into the intricate relationship between your lifestyle and mitochondrial health. By offering personalized insights and actionable recommendations, Lumen empowers you to optimize your metabolism and enhance your overall health. Remember, a key aspect of metabolic health is the ability to efficiently switch between energy sources, reflecting the adaptability and health of your mitochondria. With Lumen, you can take control of your metabolic journey and support your mitochondria in functioning at their best.
Lumen measures the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in your breath to determine whether your body is predominantly burning carbohydrates or fats for energy. The device uses a process called respiratory exchange ratio (RER) to infer this information. Here’s how it works, particularly in the context of pre- and post-workout measurements:
How Lumen Measures CO2
- Breath Sample Collection:
- Pre-Workout Measurement: Before starting a workout, you take a breath measurement using the Lumen device. This involves exhaling into the device, which then analyzes the CO2 concentration in your breath.
- Post-Workout Measurement: After completing your workout, you take another breath measurement to assess how your metabolic state has changed.
- CO2 Analysis and RER Calculation:
- The Lumen device analyzes the CO2 levels in your breath. The ratio of CO2 produced to oxygen consumed (which the device infers) gives an estimate of the RER. The RER value helps determine the predominant fuel source your body is using:
- Higher CO2 Levels (Higher RER): Indicates a higher carbohydrate utilization, as burning carbohydrates produces more CO2 relative to oxygen consumed.
- Lower CO2 Levels (Lower RER): Suggests a higher fat utilization, as burning fats produces less CO2 relative to oxygen consumed.
- The Lumen device analyzes the CO2 levels in your breath. The ratio of CO2 produced to oxygen consumed (which the device infers) gives an estimate of the RER. The RER value helps determine the predominant fuel source your body is using:
- Interpreting the Data:
- Pre-Workout State: The CO2 measurement before a workout helps determine whether your body is primarily burning fats or carbohydrates at rest. This can be influenced by factors like your previous meal, fasting state, and overall metabolic flexibility.
- Post-Workout State: The post-workout measurement reflects how your body has responded to the exercise. For example, high-intensity exercise typically leads to a higher RER due to increased carbohydrate burning, while low-intensity exercise may maintain or even lower the RER, indicating a continued reliance on fats.
Benefits of Pre- and Post-Workout CO2 Measurements
- Understanding Fuel Utilization: By comparing pre- and post-workout measurements, you can gain insights into how efficiently your body switches between fuel sources. For instance, a shift from fat to carbohydrate burning post-workout is expected during high-intensity exercise.
- Optimizing Nutrition and Training: The data from Lumen can help you tailor your nutrition and training to your metabolic state. For example, if you find that you are not efficiently switching to carbohydrate burning during intense exercise, you might adjust your carbohydrate intake before workouts.
- Tracking Metabolic Adaptations: Regular measurements allow you to monitor changes in your metabolic flexibility over time. Improvements in your ability to burn fats or carbohydrates can indicate positive adaptations to your training and lifestyle.
Conclusion:
Lumen’s CO2 measurements before and after workouts provide valuable insights into your body’s fuel utilization and metabolic flexibility. By understanding how your metabolism responds to exercise, you can make informed decisions about your diet and training, ultimately supporting better athletic performance and overall health.
How Lumen Can Help
- Lumen is a device designed to uncover the hidden connections between your lifestyle and your metabolic health.
- By using Lumen, you can identify the changes in your daily routine that will have the most significant impact on your metabolism.
- The goal isn’t to burn fat 100% of the time; rather, a healthy metabolism should burn fat at rest and during fasting, and carbohydrates during intense or sudden energy bursts.
Lumen helps determine the optimal fuel types and amounts for pre- and post-workout nutrition by analyzing your metabolic state through breath measurements. The device provides personalized nutrition recommendations based on whether your body is burning fats or carbohydrates at a given time. Here’s how it works and how it can guide your dietary choices around different types of workouts:
How Lumen Measurement Works for Nutrition Guidance
- Breath Measurement:
- Pre-Workout: Before exercising, you take a breath measurement with Lumen. The device analyzes the CO2 concentration in your breath, providing insight into your current metabolic state (whether you’re burning fats or carbohydrates).
- Post-Workout: After exercising, another breath measurement is taken to assess how your metabolism has shifted as a result of the workout.
- Interpreting the Metabolic State:
- Fat Burn (Low CO2 Levels): Indicates a predominance of fat utilization. This state is typically observed at rest or during low-intensity activities.
- Carb Burn (High CO2 Levels): Indicates a predominance of carbohydrate utilization, which is more common during high-intensity activities.
- Personalized Recommendations:
- Based on these measurements, Lumen suggests specific nutrition strategies to optimize your energy levels and recovery. This includes what type of macronutrients (fats, carbohydrates, proteins) you should consume and when.
What to Eat Before and After a Workout
Pre-Workout Nutrition
- High-Intensity Workouts (e.g., HIIT, sprints, heavy lifting):
- If in Fat-Burn Mode: Lumen may recommend consuming more carbohydrates before your workout to ensure you have enough quick-access energy for high-intensity efforts. For example, a meal or snack with easily digestible carbs like a banana, oats, or a sports drink.
- If in Carb-Burn Mode: You may already have sufficient carbohydrate stores. Lumen might suggest a balanced meal with both protein and fats, ensuring sustained energy release.
- Low-Intensity Workouts (e.g., steady-state cardio, yoga, light lifting):
- If in Fat-Burn Mode: You may not need a significant carbohydrate boost. A small, balanced snack with a mix of protein and fats, such as a handful of nuts or a small portion of yogurt, could suffice.
- If in Carb-Burn Mode: A light snack might be recommended, as the workout may not deplete your glycogen stores significantly.
Post-Workout Nutrition
- High-Intensity Workouts:
- Replenishing Glycogen: Lumen may suggest consuming carbohydrates post-workout to replenish glycogen stores depleted during exercise. For example, a smoothie with fruits, a protein shake with added carbs, or a balanced meal with a good carb source like sweet potatoes.
- Protein Intake: To aid muscle recovery, consuming a source of protein is crucial. Options could include lean meats, eggs, protein shakes, or plant-based protein sources.

- Low-Intensity Workouts:
- Balanced Recovery: A balanced post-workout meal with moderate carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats can help replenish energy without overloading on carbs. Examples include a salad with chicken and avocado or a veggie omelet with whole grain toast.
Type of Workout and Fuel Needs
- Strength Training (Anaerobic): Requires adequate carbohydrate intake to fuel intense efforts and sufficient protein for muscle recovery. Lumen may recommend higher carb intake pre- and post-workout, depending on your metabolic state.
- Endurance Training (Aerobic): A mix of carbohydrates and fats can be effective, depending on the duration and intensity. Longer, lower-intensity sessions may benefit from a higher fat intake, while higher intensity may need more carbs.
- Mixed or Interval Training: Often requires a balanced approach with both carbs and fats, alongside sufficient protein.
Conclusion:
Lumen uses real-time data on your metabolic state to provide tailored nutritional recommendations, helping you optimize energy levels, performance, and recovery. By understanding whether your body is primarily burning fats or carbs, Lumen guides you in choosing the right types and amounts of foods before and after workouts, tailored to your specific exercise type and intensity.
Carb Cycling Made Smart with Lumen
Carb cycling is a dietary strategy that alternates between high-carb and low-carb days to optimize metabolic health, enhance workout performance, support weight management, and improve the body’s ability to switch between using carbohydrates and fats as energy sources. The goal of carb cycling is to leverage the benefits of both carbohydrates and fats, depending on one’s metabolic state, activity level, and specific health or fitness goals.
How Lumen Works for Carb Cycling
Lumen, a breath analysis device, helps tailor carb cycling plans by providing real-time data on your metabolic state. Here’s how it works:
- Measuring Metabolic State:
- Breath Analysis: Lumen measures the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in your breath to determine whether you’re burning primarily fats or carbohydrates. This is indicated by the Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER).
- Personalized Feedback: Based on your RER, Lumen provides feedback on your current metabolic state, whether you’re in fat-burn or carb-burn mode.
- Guiding Carb Intake:
- Customized Recommendations: Lumen suggests whether to consume more or fewer carbs based on your metabolic state and goals. For example, if you’re predominantly burning fats, Lumen might recommend a high-carb day to replenish glycogen stores and support high-intensity workouts.
- Adjusting Carb Cycling Plans: Depending on how your body responds to different carb intakes, Lumen helps adjust the frequency and duration of low-carb and high-carb days.
- Monitoring and Adapting:
- Daily Measurements: By taking daily breath measurements, Lumen helps track changes in your metabolic state. This allows for fine-tuning your carb cycling plan in response to how your metabolism adapts.
- Identifying Patterns: Lumen identifies patterns in your metabolic response to different carb intake levels, helping you understand the most effective cycling strategy for your body.
Who Benefits from Carb Cycling with Lumen?
- Athletes and Fitness Enthusiasts:
- Athletes can use carb cycling to fuel high-intensity workouts and improve recovery. Lumen helps ensure they’re eating the right amount of carbs to support their training demands while optimizing fat burning during rest periods.
- Individuals Seeking Weight Management:
- For those aiming to lose weight or manage their weight, carb cycling can help regulate insulin levels and prevent metabolic adaptation. Lumen aids in fine-tuning carb intake to maximize fat loss without sacrificing energy levels.
- People with Metabolic Health Goals:
- Individuals looking to improve insulin sensitivity, blood sugar control, or overall metabolic flexibility can benefit from carb cycling. Lumen provides insights into how their metabolism responds to different carb levels, allowing for personalized dietary adjustments.
Mechanism of Action:
- Metabolic Flexibility Enhancement: Carb cycling, guided by Lumen’s insights, trains the body to efficiently switch between using fats and carbohydrates for energy. This adaptability, known as metabolic flexibility, is key to metabolic health.
- Insulin Sensitivity: Alternating carb intake helps manage insulin levels, enhancing insulin sensitivity and glucose utilization.
- Glycogen Replenishment and Fat Burning: High-carb days replenish glycogen stores, which are crucial for high-intensity exercise. Low-carb days encourage fat burning, especially when glycogen stores are depleted.
Carb cycling, when customized to an individual’s metabolic needs, can optimize energy utilization and support various health and fitness goals. Lumen’s real-time metabolic analysis makes it easier to tailor carb cycling plans, ensuring that the approach is both effective and adaptable to one’s unique metabolism. This personalized guidance helps navigate the complexities of carb cycling, making it a smarter and more efficient strategy for improving metabolic flexibility and overall wellness.
Key Features of Lumen
Wake Up Breath
Your morning measurement, known as the “wake-up breath,” provides a quick and accurate assessment of your metabolic state. This reading helps you determine whether your lifestyle is well-balanced and what adjustments you can make to keep your metabolism on track. Ideally, you should wake up in a fat-burning state, which indicates a good balance across four major lifestyle areas: nutrition, movement, sleep, and stress management.
Healthy mitochondria, the energy powerhouses of your cells, prefer to burn fat at rest and while fasting. Thus, waking up in a fat-burning mode is a positive indicator of metabolic health. Conversely, waking up in a carbohydrate-burning state may suggest an imbalance, such as inadequate sleep, or it could be due to factors like hormonal changes related to your menstrual cycle, illness, or not being truly at rest.
Women’s Health
Women experience significant hormonal shifts throughout their lives, notably during the menstrual cycle and menopause. These hormonal changes are closely linked to metabolism and can influence how your body processes nutrients and energy. Many symptoms that women experience at different stages of their cycle or during menopause can be traced back to these metabolic shifts.
By understanding these connections, we can tailor interventions to support metabolism and enhance metabolic flexibility. This approach can help alleviate symptoms and improve the overall quality of life for women, making Lumen a valuable tool for personalized health and wellness management.
Lumen offers a practical and personalized way to understand and improve your metabolic flexibility. By focusing on key lifestyle factors and providing real-time feedback, Lumen helps you make informed decisions to optimize your metabolic health. Whether you’re aiming to enhance your energy levels, improve weight management, or simply understand your body’s unique needs, Lumen provides the insights you need to achieve your goals.