How do you improve your VO2 Max?
The blog on Topend Sports discusses VO₂ max, a key measure of aerobic capacity that indicates the maximum amount of oxygen a person can utilize during intense exercise. VO₂ max is expressed in milliliters of oxygen per kilogram of body weight per minute (ml/kg/min). It is a critical metric for endurance athletes like runners, cyclists, and rowers.
The highest recorded VO₂ max values are typically seen in elite athletes. For example:
- Male athletes can achieve values up to 94 ml/kg/min, as seen in cross-country skier Bjørn Dæhlie.
- Female athletes can reach values as high as 77 ml/kg/min, like cyclist Jeannie Longo【6】【7】【9】.
VO₂ max is influenced by factors such as genetics, training, age, and altitude. It can be tested directly through maximal oxygen consumption tests or estimated via submaximal tests. Direct measurement requires specialized equipment, including gas analyzers and ergometers, making it more complex and costly than estimations【10】.
For a full dive into the topic, you can explore the blog here.
https://www.topendsports.com/testing/records/vo2max.htm
The data from Topend Sports highlights the range of VO₂ max scores observed in various populations, showcasing the physiological capacity of elite athletes compared to the general public:
VO₂ Max in Untrained Individuals
- Average young untrained male: ~45 ml/kg/min (or 3.5 liters/min).
- Average young untrained female: ~38 ml/kg/min (or 2.0 liters/min).
Elite Athlete VO₂ Max Scores
- World-class male endurance athletes: Often exceed 80 ml/kg/min, with rare cases above 90 ml/kg/min.
- World-class female endurance athletes: Scores can surpass 70 ml/kg/min.
Top VO₂ Max Scores (Males)
- Oskar Svendsen (Cycling): 97.5 ml/kg/min—highest recorded, measured at 18 years old.
- Espen Harald Bjerke and Bjørn Dæhlie (Cross-country skiing): Both recorded 96 ml/kg/min.
- Kilian Jornet (Ultra-endurance running): Claimed scores range from 85-92 ml/kg/min.
Top VO₂ Max Scores (Females)
- Joan Benoit (Distance running): 78.6 ml/kg/min, 1984 Olympic Marathon Champion.
- Bente Skari (Cross-country skiing): 76.6 ml/kg/min.
- Charlotte Kalla (Cross-country skiing): 74 ml/kg/min, achieved at just 20 years old.
Insights and Context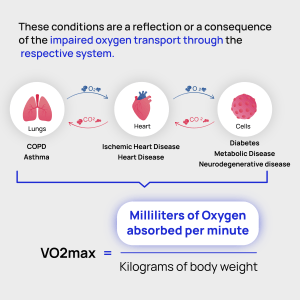
- A high VO₂ max is crucial for aerobic sports but doesn’t guarantee success. Other factors, such as technique, mental toughness, and race strategy, also play significant roles.
- The precision of these scores depends on equipment, testing protocols, and calibration, making direct comparisons tricky.
For a more detailed breakdown of these records, visit Topend Sports.
- https://youtu.be/s8BeohXl2HU?si=QNZhWTRDozGzzhxq
- https://youtu.be/sqsuJML2dkI?si=PxgThJv3LowEONnY
Episode 217 of The Peter Attia Drive podcast features Dr. Mike Joyner, a leading expert in exercise physiology, discussing strategies for improving VO₂ max and overall human performance.
This conversation ties VO₂ max improvements to better longevity and explores the following key topics:
Key Highlights:
- Peter’s 4×4 Protocol:
- Peter Attia shares his structured interval training protocol, emphasizing its effectiveness in boosting VO₂ max. The approach involves short, intense bursts of exercise with controlled recovery periods.
- Dr. Mike Joyner’s Approach:
- Joyner discusses his perspective on VO₂ max training, emphasizing the importance of tailored protocols depending on individual fitness levels, genetics, and goals.
- Exploring Your Limits with Interval Training:
- Both explore the science behind interval training’s impact on cardiovascular fitness, aerobic capacity, and overall health.
- Longevity Benefits of Improved VO₂ Max:
- The discussion connects higher VO₂ max scores with increased lifespan and enhanced healthspan, underscoring its role as a key biomarker of fitness and health.
About the Podcast:
- The Peter Attia Drive delves into optimizing longevity across physical, cognitive, and emotional dimensions. With over 70 million downloads, the podcast covers topics such as exercise, nutrition, disease prevention, and mental health.
To explore the episode further, you can visit The Peter Attia Drive.
Improving VO₂ max involves structured exercise protocols designed to challenge the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, leading to adaptations that enhance oxygen utilization. Here are evidence-based workout strategies and examples:
1. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
Description: Alternates between short bursts of intense exercise and recovery periods. HIIT is one of the most efficient ways to improve VO₂ max.
- Example Protocol:
- 4×4 Interval Training: Four intervals of 4 minutes at 90–95% of max heart rate, followed by 3 minutes of active recovery at 60–70% of max heart rate.
- Performed 3 times per week, this method has been shown to significantly boost VO₂ max in trained and untrained individuals.
2. Long Slow Distance (LSD) Training
Description: Involves exercising at a steady, moderate intensity for extended periods. While less intense than HIIT, LSD helps improve aerobic efficiency and VO₂ max over time.
- Example:
- 60–120 minutes of running or cycling at 60–70% of max heart rate.
- Often used by endurance athletes as a base-building workout.
3. Sprint Interval Training (SIT)
Description: Consists of very short, maximal effort sprints followed by longer recovery periods.
- Example Protocol:
- 30-second sprints at all-out effort, followed by 4 minutes of recovery.
- Repeat for 4–6 rounds.
- This approach has been shown to yield VO₂ max improvements comparable to traditional endurance training in less time.
4. Tempo Runs or Threshold Training
Description: Sustained efforts at or near lactate threshold intensity. These workouts help improve the body’s ability to clear lactate and sustain higher intensities.
- Example:
- 20–40 minutes of running at 80–90% of VO₂ max.
- Commonly used by runners and cyclists to build aerobic capacity and speed.
5. Fartlek Training
Description: Swedish for “speed play,” this workout combines periods of faster running with slower recovery intervals in an unstructured format.
- Example:
- During a 45-minute run, alternate between 1–2 minutes of fast running and 2–5 minutes of easy running.
- This type of training engages both aerobic and anaerobic systems.
6. Tabata Intervals
Description: A type of HIIT featuring very short, intense intervals with minimal rest. Originally designed for speed skaters, Tabata intervals improve VO₂ max quickly.
- Example Protocol:
- 20 seconds of all-out effort, 10 seconds rest.
- Repeat for 8 rounds (4 minutes total).
- Can be performed with cycling, running, or bodyweight exercises.
7. Hill Repeats
Description: Running or cycling uphill at a high intensity increases the demand on the cardiovascular system, boosting VO₂ max.
- Example:
- Sprint uphill for 30–60 seconds, then recover by walking or jogging downhill.
- Repeat for 6–10 repetitions.
8. Continuous Steady-State Training at High Intensity
Description: Sustained exercise near maximal aerobic capacity (around 90% of VO₂ max).
- Example:
- 20–30 minutes of cycling or running at a pace just below the lactate threshold.
- Often used by advanced athletes to fine-tune performance.
9. Mixed Modal Workouts
Description: Combines multiple modalities like running, rowing, and strength exercises to improve overall fitness and VO₂ max.
- Example:
- 5 rounds of:
- 500-meter row
- 10 kettlebell swings
- 400-meter run
- Rest 1–2 minutes between rounds.
- 5 rounds of:
Scientific Support:
- HIIT and SIT protocols are widely supported by studies for their efficiency in improving VO₂ max in shorter timeframes-state training is effective for building aerobic endurance and is foundational for endurance athletes .
Combining varis ensures well-rounded improvements in aerobic capacity.



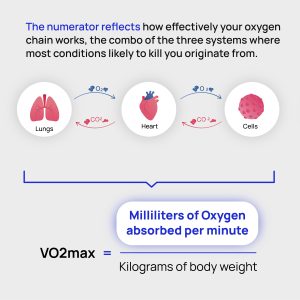
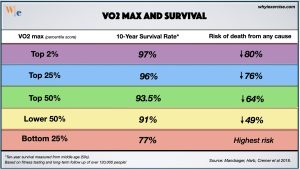

 cements
cements