Why I am suddenly gaining FAT weight?
Let’s review some definitions first and talk hormones…
Definitions & Key Concepts: Metabolism, Metabolic Health, Flexibility & Efficiency
✅ Metabolism:
Metabolism is the sum of all biochemical processes in the body that convert food into energy to sustain life. This includes:
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): Energy required for basic functions (breathing, circulation, cell repair).
- Thermic Effect of Food (TEF): Energy used to digest and absorb food.
- Physical Activity Energy Expenditure (PAEE): Calories burned through movement and exercise.
- Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT): Energy used for daily activities (walking, fidgeting).
✅ Metabolic Health:
A person is considered metabolically healthy if they have:
✔️ Stable blood sugar levels (low insulin resistance)
✔️ Efficient fat metabolism (can burn fat for energy)
✔️ Optimal body composition (higher muscle mass, lower visceral fat)
✔️ Balanced energy levels (no extreme highs/lows)
✔️ Healthy lipid profile (balanced cholesterol & triglycerides)
Poor metabolic health is linked to weight gain, insulin resistance, Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and hormone imbalances.
✅ Metabolic Flexibility:
The ability to efficiently switch between burning carbohydrates and fats for fuel based on energy demands.
- A metabolically flexible person can:
✅ Burn glucose efficiently when eating carbs.
✅ Burn fat effectively during fasting, rest, or lower-intensity activity.
✅ Avoid blood sugar crashes & energy swings.
Poor metabolic flexibility leads to:
❌ Reliance on sugar/carbs for energy (constant cravings)
❌ Insulin resistance, energy crashes, and difficulty losing fat
✅ Metabolic Efficiency:
The ability to use the least amount of oxygen & fuel to sustain activity (important for endurance & longevity).
- Efficient metabolism = Less fuel needed for the same level of performance.
- Training improves metabolic efficiency by teaching the body to use fat as a primary fuel source during lower-intensity exercise, preserving glycogen for high-intensity efforts.
Key for Aging & Endurance Athletes:
✔️ Maintain mitochondrial function
✔️ Improve fat oxidation & energy balance
✔️ Optimize VO2 max & oxygen utilization
How Aging & Hormonal Changes Impact Metabolism & Energy Production
As we age (especially in perimenopause & postmenopause), metabolism slows down due to:
❌ Declining estrogen & progesterone → Leads to insulin resistance & fat gain
❌ Loss of muscle mass (sarcopenia) → Slows BMR, reducing calorie burn
❌ Reduced mitochondrial function → Less efficient energy production
❌ Increased cortisol & stress response → Higher belly fat storage
Why Does This Happen?
- Estrogen enhances insulin sensitivity, mitochondrial function & fat oxidation → Lower estrogen = More insulin resistance & easier fat gain.
- Progesterone supports muscle recovery & stress resilience → Declining levels increase inflammation & reduce recovery ability.
- Loss of muscle = lower resting metabolic rate → Less muscle mass means fewer calories burned at rest.
Functional Medicine Solutions to Support Metabolic Health & Flexibility in Aging Women
1️⃣ Strength Training & Muscle Retention
Heavy lifting (3-5 reps) is key for metabolic rate & insulin sensitivity!
✔️ Prioritize compound movements (squats, deadlifts, presses)
✔️ Train 3-5x per week with progressive overload
✔️ Use creatine (Kion Creatine) & essential amino acids (Perfect Aminos)
2️⃣ Protein-First Nutrition Strategy
Protein = Muscle Retention = Higher Metabolism
✔️ 1.8-2.2g protein per kg BW daily
✔️ Animal-based, leucine-rich sources (grass-fed beef, eggs, wild fish)
✔️ Post-workout protein intake: 40-60g for women post-menopause
Carb Timing & Fats for Metabolic Flexibility
✔️ Carb cycling: Higher carbs on strength days, lower on recovery days
✔️ Healthy fats for hormone balance: Avocados, olive oil, grass-fed butter
3️⃣ Lifestyle Strategies for Hormone Balance
Optimize Sleep & Recovery
✔️ 7-9 hours of quality sleep → Improves insulin sensitivity & muscle recovery
✔️ Magnesium glycinate, GABA, and cortisol support
❄️ Cold Exposure (16°C) & Heat Therapy (Sauna 180°F)
✔️ Cold Plunges: Boost metabolism, increase dopamine, enhance fat burning
✔️ Sauna Therapy: Improves mitochondrial function, increases heat shock proteins
4️⃣ Functional Testing & Bio-Individuality
Testing to track metabolic & hormonal shifts
✔️ DUTCH Test (hormones & cortisol patterns)
✔️ GI-MAP Test (gut health, microbiome, estrogen detoxification)
✔️ Metabolic Testing (RMR, VO2 Max, lactate threshold)
Adjust protocols based on lab data!
Take Control of Your Metabolism & Longevity!
Aging does NOT mean inevitable weight gain or metabolic decline. It’s about strategic adaptations!
Debbie Potts Coaching offers a functional & personalized approach to help women:
✅ Optimize muscle retention & strength
✅ Improve insulin sensitivity & energy production
✅ Reduce cortisol-driven fat storage
✅ Restore hormonal balance & metabolic flexibility
Ready to optimize your metabolism & feel your best?
Let’s build your bio-individualized plan for aging strong & thriving! 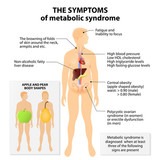
Low estrogen levels during perimenopause and menopause can contribute to weight gain through several physiological mechanisms:
1. Shift in Fat Storage
Estrogen plays a role in regulating fat distribution. When estrogen levels drop, fat storage shifts from the hips and thighs (gynoid fat distribution) to the abdomen (android fat distribution). This increase in visceral fat is associated with higher inflammation and metabolic disturbances.
2. Slower Metabolism & Reduced Muscle Mass
Estrogen helps maintain muscle mass, which is key for a higher resting metabolic rate (RMR). As estrogen declines, muscle loss accelerates (sarcopenia), leading to a slower metabolism and decreased calorie burn, making weight gain easier.
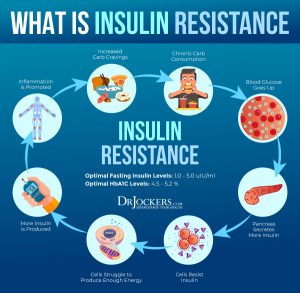
3. Insulin Resistance & Blood Sugar Dysregulation
Lower estrogen levels can contribute to insulin resistance, making it harder for the body to efficiently use glucose. This can lead to increased fat storage, particularly in the abdominal region, and a higher risk of metabolic syndrome.
4. Increased Appetite & Changes in Hunger Hormones
Estrogen influences hunger-regulating hormones like leptin and ghrelin. When estrogen drops, ghrelin (hunger hormone) increases, while leptin (satiety hormone) becomes less effective, leading to increased appetite and cravings, often for processed carbs and sugars.
5. Higher Cortisol Levels & Stress Response
Menopause is often accompanied by higher cortisol levels due to increased stress sensitivity. Elevated cortisol promotes fat storage, particularly in the midsection, and can lead to muscle breakdown, exacerbating metabolic slowdown.
6. Reduced Energy Expenditure & Activity Levels
Many women experience decreased physical activity due to joint pain, fatigue, or reduced motivation linked to hormonal changes. Lower activity levels further contribute to muscle loss and fat gain.
How to Counteract Menopausal Weight Gain?
- Strength training to preserve muscle mass and metabolic rate.
- Prioritizing protein intake (40-60g post-workout for muscle synthesis).
- Managing insulin resistance with balanced macronutrients (avoiding high-carb, low-protein meals).
- Optimizing stress response through mindfulness, breathwork, or adaptogens.
- Cold thermogenesis & heat therapy to support metabolic function and fat oxidation.
Optimizing hormones during perimenopause and menopause to counteract weight gain and metabolic changes requires a multi-faceted approach, addressing nutrition, exercise, stress, sleep, and targeted supplementation. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help balance hormones and improve body composition during this phase:
1. Strength Training & Exercise Optimization
Why? Low estrogen leads to muscle loss (sarcopenia), reduced metabolism, and increased fat storage, particularly visceral fat.
What to do:
- Prioritize resistance training: 3-5x per week, focusing on compound movements (squats, deadlifts, push-ups, pull-ups, lunges, hip thrusts).
- Incorporate HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training): 1-2x per week to improve insulin sensitivity and mitochondrial function.
- Daily low-intensity movement: Walking, yoga, or mobility work to keep stress hormones in check.
- Avoid excessive endurance training: Chronic cardio without proper recovery can increase cortisol, leading to more belly fat retention.
2. Protein & Nutritional Strategies
Why? Menopausal women have higher anabolic resistance, meaning they need more protein to trigger muscle protein synthesis.
What to do:
- Pre-Workout Fueling: 15g protein for strength training; 30g carbs for cardio sessions longer than an hour.
- Post-Workout Recovery:
- Reproductive years: 35g high-quality protein (leucine-rich) within 45 minutes.
- Perimenopause & beyond: 40-60g protein post-training due to anabolic resistance.
- Daily Protein Goal: 1.6-2.2g per kg body weight (or 0.7-1g per pound).
- Optimize Carbohydrates: Focus on whole-food sources (sweet potatoes, quinoa, lentils, berries) & avoid ultra-processed sugars that spike insulin.
- Balance Fats for Hormone Support: Include omega-3s, grass-fed meats, avocado, olive oil, nuts, and seeds for cellular function and inflammation control.
3. Managing Insulin & Blood Sugar
Why? Estrogen helps with insulin sensitivity, and its decline can lead to higher blood sugar levels, increased fat storage, and cravings.
What to do:
- Time meals strategically: Prioritize protein + fiber + healthy fats to stabilize blood sugar.
- Consider carb cycling: On strength training days, increase carbs; on rest days, reduce and emphasize healthy fats/protein.
- Use natural glucose-lowering strategies:
- Apple cider vinegar pre-meals.
- 10-minute walk after meals to reduce postprandial glucose spikes.
- Berberine or alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) as insulin-support supplements.
4. Stress & Cortisol Management
Why? Lower estrogen = higher stress reactivity → elevated cortisol → fat gain, muscle loss, poor sleep, and insulin resistance.
What to do:
- Daily mindfulness practice (breathwork, meditation, or journaling).
- Cold Thermogenesis: Dr. Stacy Sims recommends 16°C (55-56°F) for females to activate brown fat, improve insulin function, and lower inflammation.
- Heat Therapy (Sauna Use):
- Increases heat shock proteins (reducing muscle breakdown).
- Improves glucose metabolism.
- Reduces hot flashes & night sweats.
- Prioritize Sleep:
- Magnesium glycinate or L-theanine for relaxation.
- Blue light blockers to improve melatonin production.
- Keep bedroom cool & dark to enhance deep sleep.
5. Gut Health & Microbiome Balance
Why? Menopause shifts gut microbiota, increasing inflammation and estrogen metabolism dysregulation.
What to do:
- Support butyrate production: Since low Firmicutes = low butyrate, eat prebiotic fibers (onions, garlic, leeks, asparagus) & fermented foods.
- Use probiotics: Strains like Lactobacillus reuteri & Bifidobacterium help with estrogen metabolism & weight regulation.
- Check gut health: If experiencing bloating, constipation, or poor digestion, consider GI-MAP stool testing for personalized interventions.
6. Targeted Supplementation for Menopause Hormone Support
- Creatine Monohydrate (3-5g daily): Helps with muscle preservation, brain health, and energy.
- Protein Powder (Grass-Fed Whey or Plant-Based): Supports daily protein intake. (e.g., Kion Whey Protein for high-quality leucine content).
- Collagen Peptides: Supports joint, skin, and gut health.
- DHEA or Pregnenolone (Under Medical Supervision): Helps counteract low estrogen/testosterone effects.
- Adaptogens for Stress: Ashwagandha, Rhodiola, or Holy Basil help regulate cortisol.
- Magnesium Glycinate: Improves relaxation, insulin function, and sleep.
Final Thoughts on Menopausal Weight Management
Your focus should be on body recomposition, not just weight loss.
- Build muscle.
- Balance blood sugar & insulin.
- Support gut & metabolic health.
- Manage cortisol & stress effectively.
Animal-Based Nutrition Plan for Muscle & Metabolic Health
Key Principles:
✅ Prioritize protein intake (1.6-2.2g per kg of body weight).
✅ Fuel strength training with protein + carbs (not just protein alone).
✅ Incorporate healthy fats for hormone support.
✅ Avoid excessive fasting—peri/postmenopausal women benefit from stable blood sugar.
Daily Macros Focus
Protein: 40-50% (~1g per pound of body weight)
Fat: 30-40% (from high-quality animal sources)
Carbs: 10-20% (primarily from whole-food sources, timing around workouts)
Best Animal-Based Protein Sources
- Grass-fed beef & bison (rich in iron, creatine, and CLA for fat metabolism)
- Pasture-raised eggs (cholesterol supports hormone production)
- Wild-caught salmon & sardines (omega-3s for inflammation)
- Grass-fed whey protein (e.g., Kion Whey for muscle recovery)
- Organ meats (liver, heart, kidney) (micronutrient powerhouse)
- Bone broth & collagen peptides (for joint, skin, and gut health)
Workout Nutrition Strategy (Dr. Sims + Dr. Lyon Approach)
Women need more carbs around workouts than men due to estrogen’s impact on glycogen metabolism.
️♀️ Pre-Workout (30-60 min before lifting)
Strength Training Days: 15-20g protein + 30g carbs
✅ Example: 3 oz grass-fed steak + ½ banana OR 1 scoop whey protein + raw honey
Cardio Days (if included): 30-40g carbs + 15g protein
✅ Example: Greek yogurt + berries + honey
️♀️ Post-Workout (0-60 min after lifting)
Goal: Muscle protein synthesis + glycogen replenishment
Optimal: 40-60g protein + 30-50g carbs (higher post-lifting)
✅ Post-Lifting Meal Ideas:
- 6 oz grilled chicken + sweet potato mash + ghee
- 8 oz bison burger (no bun) + avocado + white rice
- 2 eggs + 4 oz steak + sourdough toast
- Kion Whey shake + raw milk + banana + cinnamon
If short on time:
- Whey shake + dates + electrolytes
Avoid high-fat meals post-workout (delays glycogen absorption).
Sample Animal-Based Meal Plan (Heavy Lifting Focus)
Breakfast (Post-Workout Meal)
- 3 pasture-raised eggs cooked in grass-fed butter
- 4 oz bison steak
- 1 cup roasted sweet potatoes
- Fermented sauerkraut for gut health
Lunch
- 6 oz grass-fed beef
- Avocado & arugula salad with olive oil
- Raw cheese & macadamia nuts
Dinner
- 8 oz wild-caught salmon or lamb chops
- Asparagus & zucchini sautéed in ghee
- ½ cup white rice or quinoa (if needed for performance)
Snacks (Optional)
- Hard-boiled eggs + beef jerky
- Bone broth + sea salt
- Raw milk kefir + collagen peptides
Heavy Lifting Plan (Strength & Hypertrophy Focus)
Lifting 4-5x per week for strength & muscle growth
️♀️ Weekly Workout Split
Day 1: Lower Body (Strength Focus)
- Squats (4×6)
- Romanian Deadlifts (4×8)
- Hip Thrusts (4×10)
- Walking Lunges (3×12)
Day 2: Upper Body (Push Focus)
- Bench Press (4×6)
- Overhead Press (4×8)
- Dips (3×10)
- Triceps Extensions (3×12)
Day 3: Rest / Active Recovery (Cold Plunge, Sauna, Walking)
Day 4: Lower Body (Glute & Hamstring Focus)
- Deadlifts (4×6)
- Bulgarian Split Squats (3×8 per leg)
- Nordic Hamstring Curls (3×10)
- Calf Raises (3×12)
Day 5: Upper Body (Pull Focus)
- Pull-Ups (4×6)
- Barbell Rows (4×8)
- Bicep Curls (3×10)
- Face Pulls (3×12)
Day 6: Optional Full-Body Strength / Mobility Work
- Heavy Kettlebell Swings
- Core & Mobility Focus
Day 7: Full Recovery (Cold Exposure + Sauna)
Recovery & Hormone Optimization
✔️ Cold Plunge (16°C / 55°F): Improves metabolism & inflammation
✔️ Sauna (180°F, 20-30 min): Supports heat shock proteins
✔️ 8+ hours sleep: Key for muscle growth & fat metabolism
✔️ Electrolytes (Sodium, Magnesium, Potassium): Prevents cramping & fatigue
Final Takeaways
✅ Dr. Lyon: Prioritize protein + resistance training for longevity.
✅ Dr. Sims: Women need carbs pre/post-training for optimal fueling.
✅ Animal-Based Approach: Focus on high-quality proteins, fats, and bioavailable micronutrients.






 trategic carb & protein intake
trategic carb & protein intake