Are you creating excessive oxidative stress?
What can you do to take ownership of your future self?
Supporting cells for athletes who experience oxidative stress due to excessive endurance exercise involves various strategies aimed at reducing oxidative damage, promoting recovery, and optimizing overall health and performance.
Here are some ways to support cells in athletes:
- Antioxidant-Rich Diet: Encourage athletes to consume a diet rich in antioxidants, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. These foods provide vitamins (such as vitamin C and vitamin E), minerals (such as selenium and zinc), and phytonutrients (such as flavonoids and carotenoids) that act as antioxidants and help neutralize free radicals.
- Supplementation: In addition to a well-balanced diet, consider supplementing athletes with antioxidants, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, selenium, and N-acetylcysteine (NAC). These supplements can help bolster the body’s antioxidant defenses and support recovery from exercise-induced oxidative stress. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional or sports nutritionist before starting any supplementation regimen, as excessive doses of certain antioxidants may have adverse effects.
- Glutathione Support: Since glutathione is a critical endogenous antioxidant, supporting its synthesis and regeneration can help enhance cellular antioxidant capacity. Encourage athletes to consume foods rich in cysteine (such as whey protein, eggs, and garlic) and other precursors of glutathione synthesis. Additionally, consider supplementing with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) or glutathione precursors like S-acetyl glutathione or liposomal glutathione to support glutathione levels.
- Hydration: Adequate hydration is crucial for cellular function and overall health, especially during and after exercise. Encourage athletes to maintain proper hydration levels by drinking water and electrolyte-rich fluids before, during, and after workouts. Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium play essential roles in cellular hydration and function.
- Rest and Recovery: Ensure athletes prioritize adequate rest and recovery between training sessions to allow for cellular repair and adaptation. Incorporate active recovery strategies such as light exercise, stretching, foam rolling, and massage to enhance circulation, reduce muscle soreness, and promote recovery.
- Periodization: Implement a well-structured training program that includes periods of varying intensity and volume (periodization). This approach helps prevent overtraining and excessive oxidative stress by allowing for adequate recovery and adaptation. Balance high-intensity workouts with lower-intensity sessions and incorporate rest days into the training schedule.
- Stress Management: Encourage athletes to manage stress levels through techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and adequate sleep. Chronic stress can exacerbate oxidative damage and impair recovery, so addressing psychological stressors is essential for overall well-being.
- Regular Monitoring: Monitor athletes’ training load, recovery status, and overall health regularly to identify signs of overtraining or excessive oxidative stress. Adjust training programs and interventions as needed to optimize performance and minimize the risk of injury or burnout.
By implementing these strategies, athletes can support their cells and mitigate the negative effects of oxidative stress associated with excessive endurance exercise, ultimately promoting better recovery, performance, and long-term health.
What is Glutathione?
Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of three amino acids: glutamine, cysteine, and glycine. It is a powerful antioxidant that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes in the body.
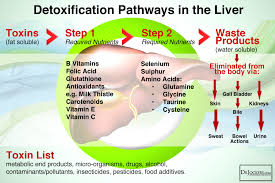
Glutathione is found in virtually every cell and is particularly concentrated in the liver, where it is involved in detoxification processes.
The synthesis of glutathione occurs in two main steps:
- Synthesis of γ-glutamylcysteine: This step is catalyzed by the enzyme γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase, which combines glutamate and cysteine to form γ-glutamylcysteine.
- Synthesis of glutathione: In the final step, γ-glutamylcysteine is combined with glycine by the enzyme glutathione synthetase to form glutathione.
Glutathione is essential for several reasons:
- Antioxidant Defense: Glutathione plays a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the body, thereby protecting cells and tissues from oxidative damage.
- Detoxification: Glutathione is involved in the detoxification of harmful substances such as heavy metals, pollutants, and drugs by facilitating their excretion from the body.
- Immune Function: Glutathione supports the proper functioning of the immune system by helping immune cells function optimally and by protecting them from oxidative damage.
- Regeneration of Other Antioxidants: Glutathione can regenerate other antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, enhancing their effectiveness in combating oxidative stress.
- Maintenance of Cellular Homeostasis: Glutathione plays a role in maintaining cellular redox balance and regulating various cellular processes, including DNA synthesis and repair, protein synthesis, and cell proliferation.
Given its importance in maintaining overall health and well-being, glutathione deficiency has been linked to various health conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, immune disorders, and aging.
Therefore, ensuring adequate levels of glutathione through diet, supplementation, or lifestyle modifications may have beneficial effects on health.
What is NAC?
What Is N-acetylcysteine (NAC)?
N-Acetylcysteine is the supplement form of Cysteine, an amino acid. Amino acids form the building blocks of proteins in the body. Cysteine is also important for the production of glutathione (the body’s most powerful antioxidant).
14 NAC Benefits
1. NAC is Needed to Make Glutathione (a powerful antioxidant)
NAC helps your body create intracellular glutathione. Glutathione is our body’s antioxidant powerhouse. Antioxidants protect our cells from free radical damage. Free radicals As I explain in this article about vitamin C, our immune system creates free radicals to defend against viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens.
How Does NAC Help Your Body Make Glutathione?
- Glutathione is made up of three amino acids: L-cysteine, L-glutamate, and glycine.
- NAC provides the L-cysteine component that enables your body to make glutathione.
- Glutathione is vital for many functions, like DNA synthesis, helping certain enzymes, supporting the immune system, and more.
- Bottom line: We need glutathione. And NAC, as one of its building blocks, is therefore very important as well.
2. May Improve Fertility in Women (and Men!)
Because of its ability to support antioxidants in the body, NAC has the potential to help with fertility in both women and men. Antioxidants help protect both egg and sperm.
NAC for Female Infertility
In a case controlled study of women struggling with unexplained infertility and undergoing intrauterine insemination, it was shown that women given 1,200 mg NAC had a higher number of follicles, as well as a higher pregnancy rate.
Continue reading because I’ll share more about fertility in the PCOS section.
NAC and Male Infertility
Men with fertility issues have higher levels of semen reactive oxygen species (a form of oxidative damage) than fertile men. This can cause sperm damage and dysfunction. In a study of 50 infertile men, who were given 600 mg NAC for 3 months, it was shown that the men’s sperm count and motility increased. Abnormal structures and DNA fragmentation decreased. It was therefore concluded that oral NAC supplementation may improve sperm quality, as well as help with the balance between oxidative stress and antioxidants in men with fertility problems.
In another study with 35 infertile men with a varicocele, the participant underwent surgery to correct the varicocele and supplemented with 600 mg NAC for 3 months. The study found a 22% increase in pregnancy rates and improved sperm quality.
3. NAC Supplementation for Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
NAC has been shown in several studies to have benefits in the management of PCOS. We understand that PCOS symptoms can include irregular cycles, weight gain, hair loss on the scalp, hair growth on the face and torso, and infertility.
In a trial involving 100 women with PCOS, NAC was compared to Metformin, a blood sugar specific drug commonly prescribed in PCOS. In this trial women were given 600 mg of NAC to be taken three times a day or 500 mg metformin three times daily. What they found was that both treatments significantly reduced menstrual irregularities, free testosterone, and hirsutism.
The study showed that NAC helped to decrease:
- BMI
- Hirsutism (meaning there was less hair on the face, chest, and abdomen—a common complaint of women with PCOS)
- Fasting insulin (there was better blood sugar balance)
- Free testosterone (unusually high levels of testosterone can lead to acne, oily skin, and hair loss)
- Menstrual irregularities
- Total and LDL cholesterol (Metformin only led to a decrease in total cholesterol)
- The study concluded that NAC was useful in the treatment of PCOS.
- In my clinical practice, I’ve had patients experience the same benefits while taking 900 mg twice daily. This reducing the risk of missed dosages and I’ve have better patient compliance with it.
- In another study, it was found that NAC supplementation improved pregnancy and ovulation rates in women with PCOS.
4. May Stabilize Blood Sugar
A study of high-fat diet-fed mice (who are glucose intolerant and insulin resistant because of their diet) was conducted. These mice presented with elevated fasting glucose levels, as well as impaired glucose disposal.
After being given NAC at specific doses, NAC improved both glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity.
In human clinical trials NAC has been studied as a short-term (2 week intervention) with no benefit to blood sugar. It’s important to note that the majority of studies showing benefit of NAC have had participants supplementing for longer periods of time (generally around 3 months). So it may be that while no benefit is seen after 2 weeks, there may be benefits with a longer duration of use.
Other studies have noted that with regards to PCOS, NAC may be beneficial in supporting healthy insulin levels. Insulin is the hormone that helps glucose (blood sugar) enter the cell.
5. Prevents Oxidative Damage and Inflammation
- Because NAC is important for the production of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant, it is also important in helping to prevent oxidative stress and inflammation.
- “Oxidative stress” is a term that gets thrown around a lot, but what is it, exactly?
- Oxidative stress refers to an imbalance between the harmful free radicals and helpful antioxidants in the body.
- When there are too many free radicals in relation to antioxidants, oxidative damage and inflammation can occur.
- That’s why it’s important for us to have as much support for our antioxidants as possible.
6. Supports a Healthy Microbiome
Your gut is where the majority of your immune system resides. So to have a healthy immune system, we need to have a healthy gut. In fact, to be healthy at all we need to have a healthy gut. After all, you are what you eat, digest, and absorb.
As I explain in Beyond the Pill, it is also a key player in hormone balance and can be impacted by the pill, leading to dysbiosis.
But as we’ll explore in this section, your gut isn’t the only place NAC may be of benefit.
Gut Microbiome
- Prevotella, as well as other organisms are known to create biofilms to protect themselves from the body’s immune system and antibiotic therapy.
- Healthy levels of Lactobacillus brevis can help lower the biofilm defense in order for the immune system to naturally eradicate unhealthy overgrowth of these organisms. However, when overgrowth of normal flora occurs (commonly referred to as dysbiosis), there may not be sufficient Lactobacilli available to inhibit biofilm production.
- This is where NAC can be of benefit!
- It is a known biofilm disruptor that can be used alongside antibiotics or antimicrobial herbs in treating the gut.
- Clinically, I have found great benefit from using NAC alongside an antimicrobial prescription in order to eradicate unhealthy levels of bacteria.
- In a systematic review it was stated, “NAC, in combination with different antibiotics, significantly promoted their permeability to the deepest layers of the biofilm, overcoming the problem of the resistance to the classic antibacterial therapeutic approach.”
- Or in other words, NAC helps the medication get to the organisms in order to elicit its effect.
- The study went on to state that because NAC is effective and safe, NAC should be considered for more widespread clinical use.
- Biofilm disruptors, like NAC, can also be useful in the treatment of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth or SIBO.
- Biofilms can be present in the gut, vagina, mouth, and in the respiratory tract.
Respiratory Tract Microbiome
- Biofilms have been cited as being associated with recurrent respiratory infections.
- In fact, Prevotella (as the example we are using here) is one of the more predominant organisms in the respiratory tract. Interestingly, some studies have shown however, that this not the case in those who suffer from asthma.
- Keep reading because I’m going to share some more respiratory specific benefits with regards to NAC.
Oral Microbiome
- In the Journal of Microbial Physiology and Biochemistry it was stated that NAC has been shown to decrease inflammation in gum tissue and has the potential to disrupt biofilms, as well as elicit and antimicrobial effect.
- More research is needed, specifically clinical trials, to understand how NAC can best be utilized as part of dental care.
7. Reduces Respiratory Symptoms in Chronic Lung Disease (like COPD)
COPD is a common lung disease resulting from chronic airflow obstruction and inflammation. While it isn’t a reversible disease, it is preventable (a major way to help prevent it is to not smoke) and treatable. When administered orally at 1200-1800 mg/day, NAC decreased COPD exacerbations.
Oxidative stress and free radicals play a role in COPD, which makes anti-inflammatory substances and antioxidants a logical choice for helping to treat and manage the condition. NAC has been shown to reduce COPD and chronic bronchitis flares.
In a 2016 review in the Journal of Respiratory Medicine it was concluded that NAC either alone or with antibiotics can decrease the risk of increased symptoms or worsening of conditions such as COPD, chronic bronchitis, and rhinosinusitis.
As with most studies regarding NAC, there is a dose dependent effect. Or in other words, if you aren’t taking enough and doing it consistently then you’re unlikely to see a benefit.
NAC is also a common prescription to be used with a nebulizer (drug is acetylcysteine) for those with COPD. This is because it also helps with the clearance of mucus from the lungs.
8. May Enhance Immune Function by Increasing Glutathione and Modulating Inflammation
As explained in the article on Vitamin C, immune cells product reactive oxygen species are part of immune defense. Unfortunately, this can also harm the very immune cells trying to defend you.
Improved Immune Function as We Age
As we age, immune function declines, which is in part due to oxidative damage and inflammation.
In a small study assassing the benefits of 600 mg/day of NAC in supporting postmenopausal women’s immune health it was concluded that:
“The present finding suggest that a short period of NAC supply (i.e., 2-4 months) at the dose used may lead to prolonged strengthening of immune defense in postmenopausal women, likely by increasing the leukocyte glutathione pool. Thus, NAC could contribute to maintenance of good health and quality of life in postmenopausal women by decreasing the probability of immune system-related diseases, such as infections, in aging.”
These conclusions were drawn because NAC supplementation led to the test group’s studied immune system parameters becoming closer to that of the control group (young, healthy females). It was concluded that NAC might exert a modulating effect on the immune system, helping it to find balance.
Immune Function in HIV Patients
Research has shown improved immune function in those supplementing with NAC. In the research, many studies have focused on human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
In one study it was stated:
“Two randomized placebo-controlled trials have shown that treatment of HIV-infected patients with N-acetyl-cysteine caused in both cases a significant increase in all immunological functions under test, including an almost complete restoration of natural killer cell activity.”
9. NAC in Influenza and Viral Illness
In cell models, NAC has been shown to inhibit replication of RNA viruses like the kind responsible for influenza A, B and RSV. It has also been shown in both cell models and human studies to inhibit inflammatory molecules.
Because of its ability to support healthy immune function, antioxidant status and support the body in modulating inflammation, NAC is an important consideration in the treatment of viral illness.
In a randomized placebo-controlled study of 262 elderly individuals without any pre-existing respiratory illness receiving 600 mg/day NAC for 6 months, it was found that the group taking NAC experienced a significant decrease in frequency of influenza-like episodes, length of time confined to a bed, and a reduction in severity of symptoms.
What may be most compelling about this study is that they found that in those using NAC, only 25% of those infected developed symptoms. In the placebo group (those not taking NAC), 79% developed symptoms. While this study does show promise, it is important to note it has not been replicated, which is important in determining the efficacy of this treatment.
More human trials are needed to understand the potential of NAC in this capacity and examine the synergistic effect of NAC alongside pharmaceutical treatment. Some studies have shown that NAC’s effectiveness is strain dependent, which means while it may help with inflammation, immune system modulation, and mucus breakdown, it may not elicit a direct effect on viral replication in all cases. Remember to always talk with your doctor before beginning new supplements.
10. NAC for Autoimmune Disease
- Many autoimmune diseases (e.g. Hashimoto’s, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, etc.) stem from inflammation in the body.
- Often, finding ways to reduce the inflammation (such as eating more vegetables, eliminating or reducing refined sugar, and limiting intake of vegetable oil) can have positive outcomes for those who suffer with autoimmune diseases.
- Supplementation can also be helpful. And that’s where NAC comes in.
- As a precursor to glutathione that helps to reduce inflammation, it is a great choice for those with autoimmune conditions who want to support their health.
- Additionally, NAC was shown in a study to inhibit inflammatory cytokines, making it a potential treatment for Th1-mediated autoimmune diseases.
- Remember, autoimmunity is complex, which is why it generally requires a holistic approach, which sometimes also includes pharmaceuticals.
11. NAC Supports Detoxification and Protects Your Kidneys and Liver
There has been a significant amount of research into the efficacy of NAC in helping with detoxification. NAC is protective of both the kidneys and liver.
Acetaminophen (commonly recognized as Tylenol) toxicity is the common cause of medication-induced hepatotoxicity. NAC is the antidote given in cases of acetaminophen toxicity.
Hepatotoxicity refers to damage to the liver caused by medications, supplements, or chemicals. NAC has been used for years as a counter-poison for acetaminophen toxicity. If a person is administered NAC within eight hours of acetaminophen overdose, their chances of recovery are great, and the danger to their liver is minimal.
Acetaminophen metabolism produces a toxin known as N-acetyl-pbenzoquinonimine, which rapidly depletes the body’s glutathione. NAC is thought to be hepatoprotective due to its antioxidant properties, is known to replenish glutathione, and can directly aid the body in metabolising N-acetyl-pbenzoquinonimine.
You know what else depletes glutathione? Alcohol. Which is why popping a Tylenol after a night of binge drinking can be a big disaster for some people.
As I explain in Beyond the Pill, NAC is important for phase 2 liver detoxification, which is a crucial step in neutralizing potential toxins created during phase 1 detoxification. Yes, your body sometimes makes toxic intermediates during this process, which is why phase 2 is so important.
Another example of how NAC can help with detoxification is in dentistry. Poly-methyl methacrylate (PMMA) resin is one of the most commonly used materials in dental practices (e.g. to make dentures). However, it has been shown to be a cytotoxin, meaning that it can result in cell damage or cell death. In a study of the dental pulp cells of rats, the addition of NAC to the PMMA resin helped improve the cytotoxicity to the dental pulp cells.
12. May Reduce Psychiatric and Addictive Disorders
Research has shown that NAC has the potential to help with the treatment of psychiatric and addictive disorders, such as nicotine addiction, OCD, trichotillomania (TTM: the compulsion to pull out body hair), schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and more.
Reduction of Trichotillomania Symptoms
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of NAC for the treatment of TTM, 50 people were given 1,200 mg of NAC or a placebo for six weeks, followed by another six weeks of 2,400 mg of NAC or a placebo. Half the people were also taking medication at the time, and a few were undergoing psychotherapy. It was found that NAC decreased the symptoms of TTM.
NAC for Schizophrenia
It has been found that, in people with schizophrenia, there is dysfunctional glutamate metabolism, as well as decreased levels of glutamate in the prefrontal cortex. Additionally, there is evidence showing that individuals with schizophrenia have oxidative stress. NAC might be helpful in the treatment of schizophrenia because it can decrease oxidative stress, as well as alleviate glutamatergic dysfunction.
NAC for OCD, Bipolar, and Depression
There have been studies showing benefits of using NAC in moderate to severe OCD. In one randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial NAC was used in addition to fluvoxamine, a common SSRI, in one treatment group. The other group received fluvoxamine and placebo. The group receiving NAC in addition to their medication experienced more improvement in symptoms compared to the placebo group.
NAC has also been found to decrease symptoms of depression and bipolar disorder. In one analysis, it was found that NAC reduced depressive symptoms and resulted in an overall increase in functionality.
While NAC does show promise in supporting mental health, you should not use NAC to replace your medication or make changes to your regimen without talking to your doctor.
13. May Improve Brain Health
NAC has been shown to ameliorate the symptoms of Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease, two diseases that affect the brain (as well as other systems in the body).
NAC for Alzheimer’s Disease
In Alzheimer’s Disease, mitochondrial dysfunction, metal accumulation, and inflammation all play a role…as well as oxidative damage. Different studies have shown that lipoic acid and NAC decreased levels of oxidative damage, while also helping to protect mitochondrial function.
Because lipoic acid and NAC can act on our mitochondria, they have a lot of potential in the treatment of Alzheimer’s. Mitochondria are a huge source of oxidative stress in neurodegeneration, so protecting them is key.
NAC for Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease is also caused by deterioration of neurons in the brain and nervous system. It has been found that most patients with Parkinson’s have oxidative damage. In animal models, treatment with NAC has led to improvements in: increased levels of glutathione in the brain, reduction of oxidative damage, and increased brain mitochondrial activities.
14. NAC May Help Prevent Heart Disease
- Oxidative damage can destroy heart tissue and lead to head attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular issues.
- Because NAC is helpful in reducing oxidative stress, it can be useful in preventing oxidative damage to tissues of the heart.
- This gives it great potential to help in the treatment and prevention of heart disease.
- NAC also improves blood flow and circulation by increasing nitric oxide production and acting as an anti-aggregate.
- An anti-aggregate prevents platelets from clumping together to form a clot in your blood vessels.
- As stated in the PCOS section of this article, NAC has also been shown to have benefits on healthy cholesterol levels.
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) Prescriptions and Supplements
- As a nebulized medication, your doctor may prescribe a 10% or 20% solution of Acetylcysteine to be used 3-4 times daily.
- For acetaminophen overdose, NAC is administered in a hospital setting via IV.
- Cetylev was a prescription effervescent NAC that was recently discontinued in early 2020.
- The good news is that NAC is easily found over the counter as a dietary supplement.
- In my practice we use N-Acetyl Cysteine supplement, which contains 900 mg of NAC.
NAC Supplementation
- If you feel you could benefit from NAC, I recommend trying our N-Acetylcysteine.
- Most people do best with one capsule 1-2 times daily.
- Remember, as discussed in this article, most benefits are achieved after several months of consistently taking NAC.
- It’s important to note that NAC does have an odor.
- So if you get a bottle and it smells “off” then know this isn’t that the NAC has gone bad…it just smells bad to some people.
How Much NAC?
- As discussed above, studies have shown that NAC benefits are dose dependent and require consistency over a period of time.
- Studies where NAC has been used for only a few weeks showed little benefit, whereas other studies have shown that NAC needs to be taken for at least a 3 month period of time to experience beneficial effects.
- The vast majority of studies have used oral NAC supplementation.
To summarize some of what has been been shown in the studies cited in this article:
- Female fertility 1,200 mg/day
- Male fertility 600 mg/day
- COPD and respiratory support 1200-1800 mg/day
- PCOS 600-1200 mg/day
- Blood sugar support 600 mg/day
- Viral illness 600 mg/day
- Immune function post-menopause 600 mg/day
It’s important to note that some of these studies used NAC along with other treatments.
Be sure to talk to your doctor about using NAC in your protocol.
https://drbrighten.com/nac-benefits/
What is NAD?
- If you’re interested in anti-aging supplements that claim to help slow the onset of disease, then look no further than those that boost levels of the coenzyme called NAD.
- What are NAD+ supplements used for? They’re used mostly for helping slow down negative effects of aging, such as chronic disease development, muscle loss and fatigue.
- As we get older, our NAD levels naturally decline, which is linked with various health problems. Research suggests that in our 20s, levels in our brain tissue start to drop. By our 40s, levels in our skin are on a decline.
- More research in humans is still needed to confirm if, and how exactly, an NAD supplement works to help promote cellular health in older adults. Based on the evidence available right now, which is mostly from mice and yeast studies, this supplement seems to help reverse mitochondrial decay, repair DNA, and supports healing of brain tissue, blood vessels and more.
What Is NAD?
What does NAD mean?
- It stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, a type of coenzyme found in humans, animals, yeast and basically all living things.
- Coenzymes are needed in the body to allow other enzymes to work.
- A basic definition of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is a cofactor found in all living cells.
- It’s involved in energy metabolism and a number of bodily processes that allow life to be possible.
- According to a 2020 study, NAD+ can directly and indirectly influence many key cellular functions, including metabolic pathways, DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, cellular senescence and immune cell function.
- NAD+ is made up of two nucleotides, the building blocks for nucleic acids, which form DNA.
Studies have linked the use of an NAD supplement with healthy aging benefits such as:
- Improved energy, mental clarity and alertness, due to its positive effects of cellular processes that support cognitive function
- Improved memory and help treating Alzheimer’s disease and dementia
- Enhanced athletic performance and muscle function
- Better protection against certain cardiovascular problems
- Reduced symptoms associated with chronic fatigue syndrome
- Protection against vision loss and signs of skin aging
- Regulation of circadian rhythms and appetite
What’s the difference between NAD and NAD+?
What is NAD+, and how is its function different than that of NAD’s?
- The difference all comes down to the charge of these coenzymes.
- NAD+ is written with a superscript + sign because of the positive charge on one of its nitrogen atoms.
- It is the oxidized form of NAD.
- It’s considered “an oxidizing agent” because it accepts electrons from other molecules.
- Although they are different chemically, these terms are mostly used interchangeably when discussing their health benefits.
- Another term you may come across is NADH, which stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) + hydrogen (H).
- This is also used interchangeably with NAD+ for the most part.
- Both are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotides that function as either hydride donors or hydride acceptors. The difference between these two is that that NADH becomes NAD+ after it donates an electron to another molecule.
NAD Precursors
Precursors are molecules used in chemical reactions inside the body to create other compounds.
There are a number of precursors of NAD+ that result in higher levels when you consume enough of them.
Our body synthesizes NAD+ from five different precursors which can be obtained through diet:
- Nicotinamide riboside (NR)
- Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN)
- Nicotinic acid (NA)
- Nicotinamide (NAM)
- Tryptophan
Some of the most important precursors for increasing NAD levels are various forms of vitamin B3: nicotinic acid (niacin), NAM and NR.
Meanwhile, NR is considered by some experts to be the most efficient precursor to NAD+.
- One study found that one single dose of NR could increase NAD+ levels in humans 2.7-fold.
- Other forms of vitamin B3 that seem to be less effective for boosting levels are nicotinic acid and nicotinamide.
How Your Body Uses NAD
- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is described as a “helping molecule” because it binds to other enzymes and causes reactions in the body that have positive outcomes on your health.
- Other factors that make this coenzyme so important for healthy aging include its effects on sirtuin “anti-aging” proteins, mitochondrial activity, and involvement in regulating oxidative stress (a cause of many chronic diseases) and circadian rhythms (our “internal clocks”).
- According to an article published in Scientific America, “A prominent theory of aging holds that decaying of mitochondria is a key driver of aging.”
- As mitochondria lose some of their power, this seems to contribute to diseases and symptoms tied to aging, including heart failure, cognitive decline/neurodegeneration and fatigue.
- Mitochondria are specialized structures found in cells. They participate in many cellular processes, including helping to extract the energy that is stored in nutrients and transforming it into a form of energy that can power the body’s cells.
- A study in mice found that increased NAD+ levels could restore mitochondrial function. NAD+ has a key role in mitochondrial function because it is the main coenzyme responsible for the delivery of the electrons that are extracted from food to the electron transport chain for ATP production.
- It is therefore as important for cellular energy as ATP itself.
NAD+ and Sirtuins
- A group of proteins that are linked with anti-aging effects, called sirtuins, rely on NAD+ to function properly.
- Sirtuins have been found to play a role in regulating cellular and mitochondrial health.
- Some animal studies show that they play a role in maintaining the length of telomeres, which is linked to longevity.
- In studies conducted using yeast, activation of sirtuin proteins has been shown to help expand life span, although we still don’t know exactly how this carries over to humans.
- Another enzyme with potential anti-aging effects is called poly (ADP-Ribose) polymerases (PARPs), which some studies shown NAD+ can also help activate.
NAD Benefits
Molecules that can be taken in supplement form to increase NAD levels in the body are referred to by some as “NAD boosters.”
Studies conducted over the past six decades suggest that the following are some of the many benefits associated with taking an NAD supplement:
1. Can Help Restore Mitochondrial Function
According to a 2021 Molecular Metabolism study, for NAD+ depletion associated with aging-related neurodegenerative disorders, NAD supplements, treatment with NAD+ precursors or sirtuin activators may help restore mitochondrial function.
2. May Help Repair Blood Vessels
NAD supplementation may aid in repair and growth of aged blood vessels. There’s also some evidence it can help manage heart disease risk factors like high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
Essentially, some NAD+ precursors — nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) — have the potential to be vasoprotective. That means they can act to alleviate or prevent conditions or diseases that affect the blood vessels. One study demonstrated that these precursors presented an effective vasoprotective mechanism to maintain healthy endothelial cells.
3. May Improve Muscle Function
A 2020 study with patients who had a systemic NAD+ deficiency were administered an increasing dose of NAD+-booster niacin (a vitamin B3 form of 750–1,000 mg/day) for 10 months.
As expected, blood NAD+ levels increased in all subjects, up to 8-fold, while muscle NAD+ of patients reached the level of their controls. Muscle strength and mitochondrial biogenesis increased in all subjects. Niacin turns out to be an efficient NAD+ booster for treating mitochondrial myopathy.
4. Potentially Helps Repair Cells and Damaged DNA
Some studies have found evidence that NAD+ precursor supplementation leads to an increase in DNA damage repair. NAD+ is broken down into two component parts, nicotinamide and ADP-ribose, which combine with proteins to repair cells.
A 2022 study noted that NAD+ helped regulate various aspects of DNA integrity, damage repair and gene expression.
5. May Help Improve Cognitive Function
Several studies conducted on mice have found that mice treated with NAD+ precursors experienced improvements in cognitive function, learning and memory. Findings have led researchers to believe that NAD supplement may help protect against cognitive decline/Alzheimer’s disease.
The 2021 Molecular Metabolism study above also found that NAD supplementation can enhance neuronal function, which can improve cognitive function.
6. May Help Prevent Age-Related Weight Gain
A 2012 study showed that when mice fed a high-fat diet were given an NAD supplement, they gained 60 percent less weight than they did on the same diets without the supplement. One reason this may be true is that nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide helps regulate production of stress- and appetite-related hormones, thanks to its effects on circadian rhythms.
Types and Dosage Recommendations
- According to a 2022 Frontiers in Nutrition study, healthy volunteers received 250 mg/day of the NAD precursor NMN for 12 weeks and were about to tolerate it safely. NAD+ blood levels were significantly increased.
- The precursor nicotinamide riboside (NR), also called niagen, is available in tablet or capsule form. A typical dosage of NR supplements is about 200 to 350 milligrams, taken once or twice daily. In studies, doses of 100, 300 and 1,000 milligrams of NR daily have been shown to have positive effects and produce dose-dependent increases in blood levels of NAD+.
- Doctors will sometimes prescribe higher doses of NAD therapy for patients in the form of intramuscular (IM) or intravenous (IV) NAD injections. This type of treatment may be used to manage symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, dementia or depression, for example.
Other Ways to Increase Levels
Humans get NAD+ from their diets, specifically from eating protein-rich foods (foods made up of amino acids). Your diet can provide you with not only amino acids and vitamin B3, but also other precursors of this coenzyme, including tryptophan and nicotinamide mononucleotide (or NMN).
Here’s how to increase NAD levels naturally:
- Consume cow’s milk, yeast and beer, which research shows all contain small amounts of NAD precursors
- Consume high-protein foods
- Consider trying the keto diet to increase ketone levels, which may increase NAD levels, according to studies
- Consider using the herbal supplement yohimbe
- Exercise regularly
- Incorporate intermittent fasting into your routine
- Avoid high alcohol intake
Precautions and Side Effects
NAD supplement options are generally well-tolerated and don’t seem to pose much risk for side effects when used for durations of about 12 to 24 weeks. Certain side effects are still possible, however, and may include nausea, fatigue, headaches, diarrhea, stomach discomfort and indigestion.
Final Thoughts
- What is NAD? It stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, which is a coenzyme found in cells of all living beings.
- NAD supplement treatments have gained attention recently as potential anti-aging compounds.
- Nicotinamide riboside (NR) seems to be the most important precursor of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide that helps increase levels. NR is an alternative form of vitamin B3 that can be taken as a supplement.
- Here’s how to increase levels naturally: Consume cow’s milk, yeast and beer (in moderation); eat foods with protein and B vitamins; fast; exercise regularly; avoid high alcohol consumption.
What is Tru Niagen?
Where True Energy Is Generated
- Mitochondrial dysfunction is one of the hallmarks of aging.
- The mitochondria are responsible for generating about 90% of the energy your body uses.
- We like to call them the “energy engines” of your cells.
- The energy they produce fuels all of our vital functions.
- They do this by converting the nutrients we get from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) via a series of complex processes.
- The process of energy generation by the mitochondria requires NAD+ in constant supply.
NAD+ for Cellular Repair and Regeneration
- NAD+ also plays an essential role in the processes of cellular repair and regeneration.
- NAD+ molecules activate sirtuins, a family of seven proteins that help to regulate cellular homeostasis, and drive the process of repair.
- Sirtuins cannot function absent the presence of NAD+.
- Enzymes called PARPs (which stands for poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase) are also dependent on NAD+ to help repair cellular DNA damage due to oxidative stress.
NAD+ Is Critical for Cellular Health
Unfortunately, NAD+ is depleted over time as you age. It’s also depleted by a range of physiological stressors, and can also fluctuate if you’re under immune stress. It’s also worth noting that as we age, we produce less mitochondria to fuel our cells—which means the ones we have need to work harder. All of this equates to what we experience as the aging process.
But mitochondrial health can be influenced by lifestyle habits, and also by using supplementation to boost your NAD+ levels. That’s where Tru Niagen comes in.
https://www.truniagen.com/science/